该文章内容发布已经超过一年,请注意检查文章中内容是否过时。
14-Dubbo配置加载全解析
14-Dubbo配置加载全解析
14.1 回到启动器的初始化过程
在应用程序启动的时候会调用发布器的启动方法 ,然后调用初始化方法,在发布器DefaultApplicationDeployer中的初始化方法initialize() 如下:
@Override
public void initialize() {
if (initialized) {
return;
}
// Ensure that the initialization is completed when concurrent calls
synchronized (startLock) {
if (initialized) {
return;
}
// register shutdown hook
registerShutdownHook();
startConfigCenter();
loadApplicationConfigs();
initModuleDeployers();
// @since 2.7.8
startMetadataCenter();
initialized = true;
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info(getIdentifier() + " has been initialized!");
}
}
}
初始化过程中会先启动配置中心配置信息处理,然后 调用加载初始化应用程序配置方法loadApplicationConfigs();进行配置加载 关于配置的官方文档链接为 配置概述
Dubbo框架的配置项比较繁多,为了更好地管理各种配置,将其按照用途划分为不同的组件,最终所有配置项都会汇聚到URL中,传递给后续处理模块。
常用配置组件如下:
- application: Dubbo应用配置
- registry: 注册中心
- protocol: 服务提供者RPC协议
- config-center: 配置中心
- metadata-report: 元数据中心
- service: 服务提供者配置
- reference: 远程服务引用配置
- provider: service的默认配置或分组配置
- consumer: reference的默认配置或分组配置
- module: 模块配置
- monitor: 监控配置
- metrics: 指标配置
- ssl: SSL/TLS配置
配置还有几个比较重要的点:
配置来源 从Dubbo支持的配置来源说起,默认有6种配置来源:
- JVM System Properties,JVM -D 参数
- System environment,JVM进程的环境变量
- Externalized Configuration,外部化配置,从配置中心读取
- Application Configuration,应用的属性配置,从Spring应用的Environment中提取"dubbo"打头的属性集
- API / XML /注解等编程接口采集的配置可以被理解成配置来源的一种,是直接面向用户编程的配置采集方式
- 从classpath读取配置文件 dubbo.properties
覆盖关系
下图展示了配置覆盖关系的优先级,从上到下优先级依次降低: 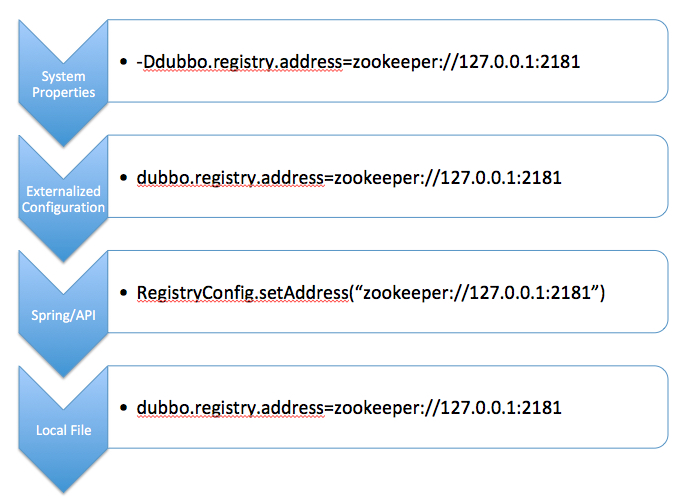
配置方式
- Java API配置
- XML配置
- Annotation配置
- 属性配置
配置虽然非常多,但是我们掌握一下配置加载的原理,再了解下官网的文档说明路径应该基础的配置搞定是没问题的,更深入的配置很多参数还是需要了解下源码的.
14.2 配置信息的初始化回顾
前面我们在讲ModuleModel对象的创建的时候ModuleModel模型中包含了一个成员变量为ModuleEnvironment 代表当前的模块环境和ModuleConfigManager配置管理器 而ModuleModel模型对象的父模型对象ApplicationModel中包含了一个成员变量Environment环境和ConfigManager配置管理器.
在回顾调用过程之前我们先看下模型,配置管理器和环境与配置之间的关系如下图:
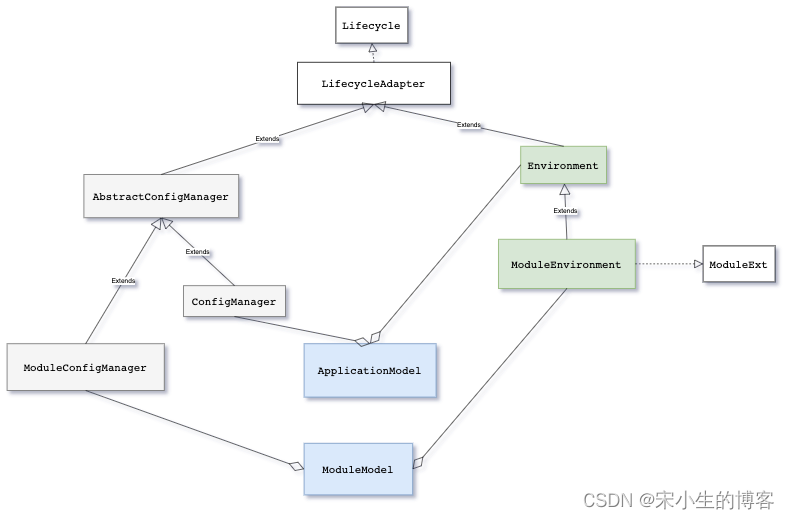
在ModuleModel对象初始化方法initialize()中创建了模块配置管理器:ModuleConfigManager 如下代码所示:
@Override
protected void initialize() {
super.initialize();
this.serviceRepository = new ModuleServiceRepository(this);
this.moduleConfigManager = new ModuleConfigManager(this);
this.moduleConfigManager.initialize();
ModuleEnvironment环境信息对象也会在配置管理器创建的时候被调用到: 如下代码所示:
@Override
public ModuleEnvironment getModelEnvironment() {
if (moduleEnvironment == null) {
moduleEnvironment = (ModuleEnvironment) this.getExtensionLoader(ModuleExt.class)
.getExtension(ModuleEnvironment.NAME);
}
return moduleEnvironment;
}
在扩展对象ExtensionLoader进行对象ModuleEnvironment创建之后会对对象进行初始化调用 initExtension(instance)方法 初始化的时候调用如下代码: ExtensionLoader中的初始化方法如下:
private void initExtension(T instance) {
if (instance instanceof Lifecycle) {
Lifecycle lifecycle = (Lifecycle) instance;
lifecycle.initialize();
}
}
14.3 属性加载
14.3.1 Environment中属性的初始化方法
这个初始化方法对应ModuleEnvironment的父类型Environment中的初始化方法如下:initialize()
@Override
public void initialize() throws IllegalStateException {
if (initialized.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
//加载在JVM或者环境变量指定的dubbo.properties配置文件 配置的key为dubbo.properties.file ,如果未指定则查找类路径下的dubbo.properties
this.propertiesConfiguration = new PropertiesConfiguration(scopeModel);
//系统JVM参数的配置无需我们来加载到内存,系统已经加载好了放到了System中,我们只需System.getProperty(key)来调用
this.systemConfiguration = new SystemConfiguration();
//系统环境变量的配置,无需我们来加载到内存,系统已经加载好了放到了System中,我们只需System.getenv(key)来获取就可以
this.environmentConfiguration = new EnvironmentConfiguration();
//从远程配置中心的全局配置获取对应配置
this.externalConfiguration = new InmemoryConfiguration("ExternalConfig");
//从远程配置中心的应用配置获取对应配置
this.appExternalConfiguration = new InmemoryConfiguration("AppExternalConfig");
//应用内的配置比如: Spring Environment/PropertySources/application.properties
this.appConfiguration = new InmemoryConfiguration("AppConfig");
//加载迁移配置,用户在JVM参数或者环境变量中指定的dubbo.migration.file,如果用户未指定测尝试加载类路径下的dubbo-migration.yaml
loadMigrationRule();
}
}
14.4.2 属性变量说明
前面我们已经基本上介绍了各个属性的含义下面用一个表格列举一下方便查看:
| 属性变量名 | 属性类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| propertiesConfiguration | PropertiesConfiguration | dubbo.properties文件中的属性 |
| systemConfiguration | SystemConfiguration | JVM参数 启动进程时指定的 (-D)配置 |
| environmentConfiguration | EnvironmentConfiguration | 环境变量中的配置 |
| externalConfiguration | InmemoryConfiguration | 外部配置全局配置 例如配置中心中 config-center global/default config |
| appExternalConfiguration | InmemoryConfiguration | 外部的应用配置 例如配置中心中执行的当前应用的配置 config-center app config |
| appConfiguration | InmemoryConfiguration | 来自应用中的配置例如:Spring Environment/PropertySources/application.properties |
| globalConfiguration | CompositeConfiguration | 前面6个配置属性放到一起就是这个 |
| globalConfigurationMaps | List<Map<String, String» | 最前面的6个属性转换为map放到一起就是这个可以理解为将全局配置globalConfiguration转换成了列表 这个列表顺序在这里是:SystemConfiguration -> EnvironmentConfiguration -> AppExternalConfiguration -> ExternalConfiguration -> AppConfiguration -> AbstractConfig -> PropertiesConfiguration |
| defaultDynamicGlobalConfiguration | CompositeConfiguration | 这个也是一个组合配置将defaultDynamicConfiguration动态配置(来自配置中心的配置)和全局配置添加到了自己的配置列表中 列表顺序为defaultDynamicConfiguration -> globalConfiguration |
| localMigrationRule | String | ,用户在JVM参数或者环境变量中指定的dubbo.migration.file,如果用户未指定测尝试加载类路径下的dubbo-migration.yaml |
关于每个配置信息这里还是来了解下细节,方便大家了解原理.
14.3.3 dubbo.properties配置文件加载解析原理
如前面所示:
//加载在JVM或者环境变量指定的dubbo.properties配置文件 配置的key为dubbo.properties.file ,如果未指定则查找类路径下的dubbo.properties
this.propertiesConfiguration = new PropertiesConfiguration(scopeModel);
下面就直接提构造器的PropertiesConfiguration代码了:
public PropertiesConfiguration(ScopeModel scopeModel) {
this.scopeModel = scopeModel;
refresh();
}
public void refresh() {
//配置获取的过程是借助工具类ConfigUtils来获取的
properties = ConfigUtils.getProperties(scopeModel.getClassLoaders());
}
继续看ConfigUtils的getProperties方法:
public static Properties getProperties(Set<ClassLoader> classLoaders) {
//这个配置的KEY是dubbo.properties.file System.getProperty是从JVM参数中获取配置的 一般情况下我们在启动Java进程的时候会指定Dubbo配置文件 如配置:
//-Ddubbo.properties.file=/dubbo.properties
String path = System.getProperty(CommonConstants.DUBBO_PROPERTIES_KEY);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(path)) {
//优先级最高的JVM参数拿不到数据则从 环境变量中获取,这个配置key也是dubbo.properties.file System.getenv是从环境变量中获取数据
//例如我们在环境变量中配置 dubbo.properties.file=/dubbo.properties
path = System.getenv(CommonConstants.DUBBO_PROPERTIES_KEY);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(path)) {
//如果在JVM参数和环境变量都拿不到这个配置文件的路径我们就用默认的吧
//默认的路径是类路径下的资源文件 这个路径是: dubbo.properties
path = CommonConstants.DEFAULT_DUBBO_PROPERTIES;
}
}
return ConfigUtils.loadProperties(classLoaders, path, false, true);
}
路径获取之后加载详细的配置内容:
ConfigUtils的loadProperties代码如下:
ConfigUtils.loadProperties(classLoaders, path, false, true);
代码如下:
public static Properties loadProperties(Set<ClassLoader> classLoaders, String fileName, boolean allowMultiFile, boolean optional) {
Properties properties = new Properties();
// add scene judgement in windows environment Fix 2557
//检查文件是否存在 直接加载配置文件如果加载到了配置文件则直接返回
if (checkFileNameExist(fileName)) {
try {
FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(fileName);
try {
properties.load(input);
} finally {
input.close();
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.warn("Failed to load " + fileName + " file from " + fileName + "(ignore this file): " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
return properties;
}
//为什么会有下面的逻辑呢,如果仅仅使用上面的加载方式只能加载到本系统下的配置文件,无法加载封装在jar中的根路径的配置
Set<java.net.URL> set = null;
try {
List<ClassLoader> classLoadersToLoad = new LinkedList<>();
classLoadersToLoad.add(ClassUtils.getClassLoader());
classLoadersToLoad.addAll(classLoaders);
//这个方法loadResources在扩展加载的时候说过
set = ClassLoaderResourceLoader.loadResources(fileName, classLoadersToLoad).values().stream().reduce(new LinkedHashSet<>(), (a, i) -> {
a.addAll(i);
return a;
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Fail to load " + fileName + " file: " + t.getMessage(), t);
}
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(set)) {
if (!optional) {
logger.warn("No " + fileName + " found on the class path.");
}
return properties;
}
if (!allowMultiFile) {
if (set.size() > 1) {
String errMsg = String.format("only 1 %s file is expected, but %d dubbo.properties files found on class path: %s",
fileName, set.size(), set);
logger.warn(errMsg);
}
// fall back to use method getResourceAsStream
try {
properties.load(ClassUtils.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(fileName));
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.warn("Failed to load " + fileName + " file from " + fileName + "(ignore this file): " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
return properties;
}
logger.info("load " + fileName + " properties file from " + set);
for (java.net.URL url : set) {
try {
Properties p = new Properties();
InputStream input = url.openStream();
if (input != null) {
try {
p.load(input);
properties.putAll(p);
} finally {
try {
input.close();
} catch (Throwable t) {
}
}
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.warn("Fail to load " + fileName + " file from " + url + "(ignore this file): " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
return properties;
}
完整的配置加载流程这里用简单的话描述下:
- 项目内配置查询
- 路径查询
- 从JVM参数中获取配置的 dubbo.properties.file配置文件路径
- 如果前面未获取到路径则从环境变量参数中获取配置的dubbo.properties.file配置文件路径
- 如果前面未获取到路径则使用默认路径dubbo.propertie
- 配置加载
- 将路径转为FileInputStream 然后使用Properties加载
- 路径查询
- 依赖中的配置扫描查询
- 使用类加载器扫描所有资源URL
- url转InputStream 如 url.openStream() 然后使用Properties加载
14.3.4 加载JVM参数的配置
这里我们继续看SystemConfiguration配置的加载 这个直接看下代码就可以了:
这个类型仅仅是使用System.getProperty来获取JVM配置即可
public class SystemConfiguration implements Configuration {
@Override
public Object getInternalProperty(String key) {
return System.getProperty(key);
}
public Map<String, String> getProperties() {
return (Map) System.getProperties();
}
}
14.3.5 加载环境变量参数的配置
这里我们来看EnvironmentConfiguration,这里我们直接来看代码:
public class EnvironmentConfiguration implements Configuration {
@Override
public Object getInternalProperty(String key) {
String value = System.getenv(key);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(value)) {
value = System.getenv(StringUtils.toOSStyleKey(key));
}
return value;
}
public Map<String, String> getProperties() {
return System.getenv();
}
}
14.3.6 内存配置的封装:InmemoryConfiguration
这里我们看下InmemoryConfiguration的设计,这个直接看代码吧内部使用了一个LinkedHashMap来存储配置
public class InmemoryConfiguration implements Configuration {
private String name;
// stores the configuration key-value pairs
private Map<String, String> store = new LinkedHashMap<>();
public InmemoryConfiguration() {
}
public InmemoryConfiguration(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public InmemoryConfiguration(Map<String, String> properties) {
this.setProperties(properties);
}
@Override
public Object getInternalProperty(String key) {
return store.get(key);
}
/**
* Add one property into the store, the previous value will be replaced if the key exists
*/
public void addProperty(String key, String value) {
store.put(key, value);
}
/**
* Add a set of properties into the store
*/
public void addProperties(Map<String, String> properties) {
if (properties != null) {
this.store.putAll(properties);
}
}
/**
* set store
*/
public void setProperties(Map<String, String> properties) {
if (properties != null) {
this.store = properties;
}
}
public Map<String, String> getProperties() {
return store;
}
}
14.3.7 Dubbo迁移新版本的配置文件加载dubbo-migration.yaml
关于配置迁移文件的用法可以看下这个Dubbo官方的地址迁移规则说明
这个配置文件的文件名字为:dubbo-migration.yaml
这个和14.3.4加载JVM参数配置的过程是相似的细节可以看14.3.4节
private void loadMigrationRule() {
//JVM参数的dubbo.migration.file配置
String path = System.getProperty(CommonConstants.DUBBO_MIGRATION_KEY);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(path)) {
//环境变量的dubbo.migration.file配置
path = System.getenv(CommonConstants.DUBBO_MIGRATION_KEY);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(path)) {
//默认的迁移配置文件 dubbo-migration.yaml
path = CommonConstants.DEFAULT_DUBBO_MIGRATION_FILE;
}
}
this.localMigrationRule = ConfigUtils.loadMigrationRule(scopeModel.getClassLoaders(), path);
}
14.4 初始化加载应用配置
加载配置涉及到了配置优先级的处理,
下面来看加载配置代码 loadApplicationConfigs()方法
private void loadApplicationConfigs() {
//发布器还是不处理配置加载的逻辑还是交给配置管理器
configManager.loadConfigs();
}
配置管理器加载配置:
@Override
public void loadConfigs() {
// application config has load before starting config center
// load dubbo.applications.xxx
//加载应用配置
loadConfigsOfTypeFromProps(ApplicationConfig.class);
// load dubbo.monitors.xxx
//加载监控配置
loadConfigsOfTypeFromProps(MonitorConfig.class);
// load dubbo.metrics.xxx
//加载指标监控配置
loadConfigsOfTypeFromProps(MetricsConfig.class);
// load multiple config types:
// load dubbo.protocols.xxx
//加载协议配置
loadConfigsOfTypeFromProps(ProtocolConfig.class);
// load dubbo.registries.xxx
loadConfigsOfTypeFromProps(RegistryConfig.class);
// load dubbo.metadata-report.xxx
//加载元数据配置
loadConfigsOfTypeFromProps(MetadataReportConfig.class);
// config centers has bean loaded before starting config center
//loadConfigsOfTypeFromProps(ConfigCenterConfig.class);
//刷新配置
refreshAll();
//检查配置
checkConfigs();
// set model name
if (StringUtils.isBlank(applicationModel.getModelName())) {
applicationModel.setModelName(applicationModel.getApplicationName());
}
}
原文地址:Dubbo配置加载全解析