Architecture
RPC communication
Dubbo3’s Triple protocol is built on the HTTP/2 protocol, so it has better penetration and versatility. The Triple protocol is compatible with gRPC and provides communication models such as Request Response, Request Streaming, Response Streaming, and Bi-directional Streaming; from Triple Starting from the agreement, Dubbo also supports IDL-based service definition.
In addition, Dubbo also integrates most of the industry’s mainstream protocols, allowing users to use these communication protocols within the Dubbo framework, providing users with a unified programming model and service governance model, these protocols include rest, hessian2, jsonrpc, thrift, etc. , note that there will be some differences in the range supported by different language SDK implementations.
Details can be viewed
Service Discovery
Service discovery, that is, the ability of the consumer to automatically discover the list of service addresses, is a key capability that the microservice framework needs to have. With the help of automated service discovery, microservices can be implemented without knowing the deployment location and IP address of the peer. communication.
There are many ways to realize service discovery. Dubbo provides a Client-Based service discovery mechanism. Usually, additional third-party registry components need to be deployed to coordinate the service discovery process, such as the commonly used [Nacos](https:/ /nacos.io/), Consul, Zookeeper, etc. Dubbo itself also provides the connection to various registry components, and users can choose flexibly.
Dubbo is based on the automatic service discovery capability of the consumer, and its basic working principle is as follows:
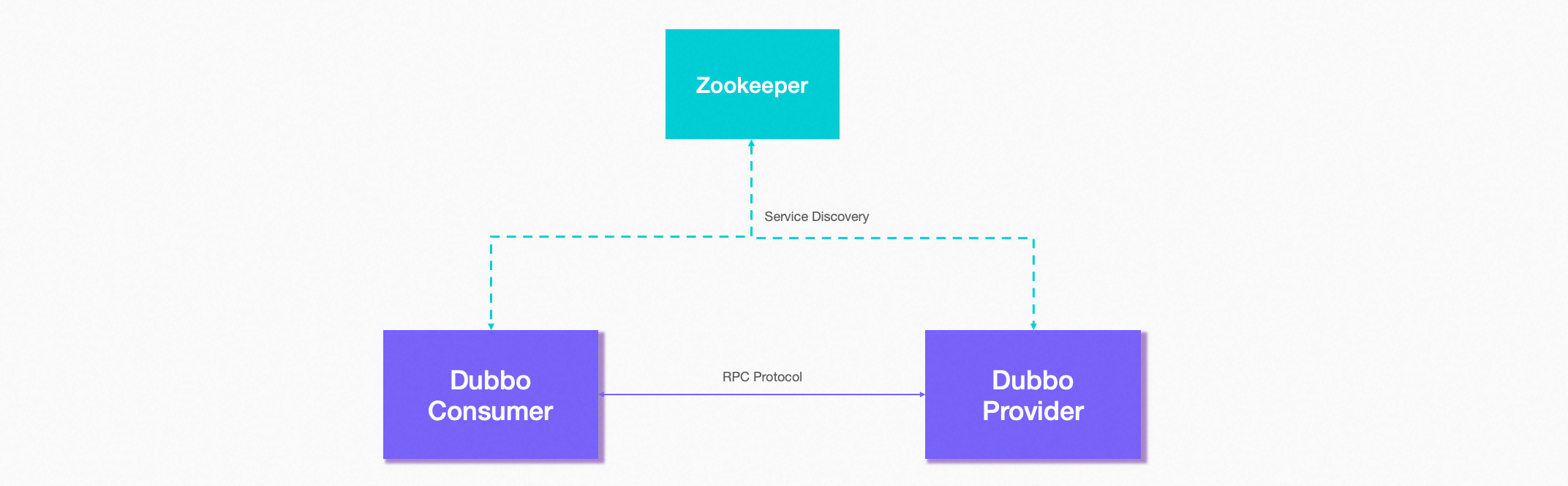
Under the traditional deployment architecture, service discovery involves three participating roles: provider, consumer, and registration center. Among them, the provider registers the URL address to the registration center, the registration center is responsible for aggregating data, and the consumer subscribes to the URL address from the registration center. renew. In the context of cloud native, for example, when the application is deployed on a platform such as Kubernetes, since the platform itself maintains the mapping relationship between the application/service and the instance, the registration center and the registration action are sinked to the infrastructure layer to a certain extent, so the framework Own registration action is sometimes not necessary.
Dubbo3 provides a new application-level service discovery model, which is different from Dubbo2’s interface-level service discovery model in terms of design and implementation. It can be viewed here:
- [Application-level service discovery](/en/docs3-v2/java-sdk/concepts-and-architecture/service-discovery/#Introduction to application-level service discovery)
Traffic management
Since Dubbo2, Dubbo has provided rich service governance rules, including routing rules, dynamic configuration, etc.
On the one hand, Dubbo3 is connecting to the governance rules represented by VirtualService and DestinationRule used in popular Mesh products such as Istio by docking xDS; on the other hand, Dubbo is seeking to design a set of its own rules to achieve Traffic governance, and flexible governance capabilities.
- Dubbo2 Service Governance Rules
- Dubbo3 service governance rules
Dubbo Mesh
The goal of Dubbo Mesh is to provide a complete Mesh solution adapted to the Dubbo system, including customized control plane (Control Plane) and customized data plane solutions. The Dubbo control plane is based on the industry’s mainstream Istio extension, and supports richer traffic governance rules, Dubbo application-level service discovery models, etc. The Dubbo data plane can use Envoy Sidecar, which implements the deployment solution of Dubbo SDK + Envoy, or Dubbo Proxyless mode. Directly realize the communication between Dubbo and the control plane. Dubbo Mesh is undergoing rapid evolution, we will try our best to keep the content of the document updated.
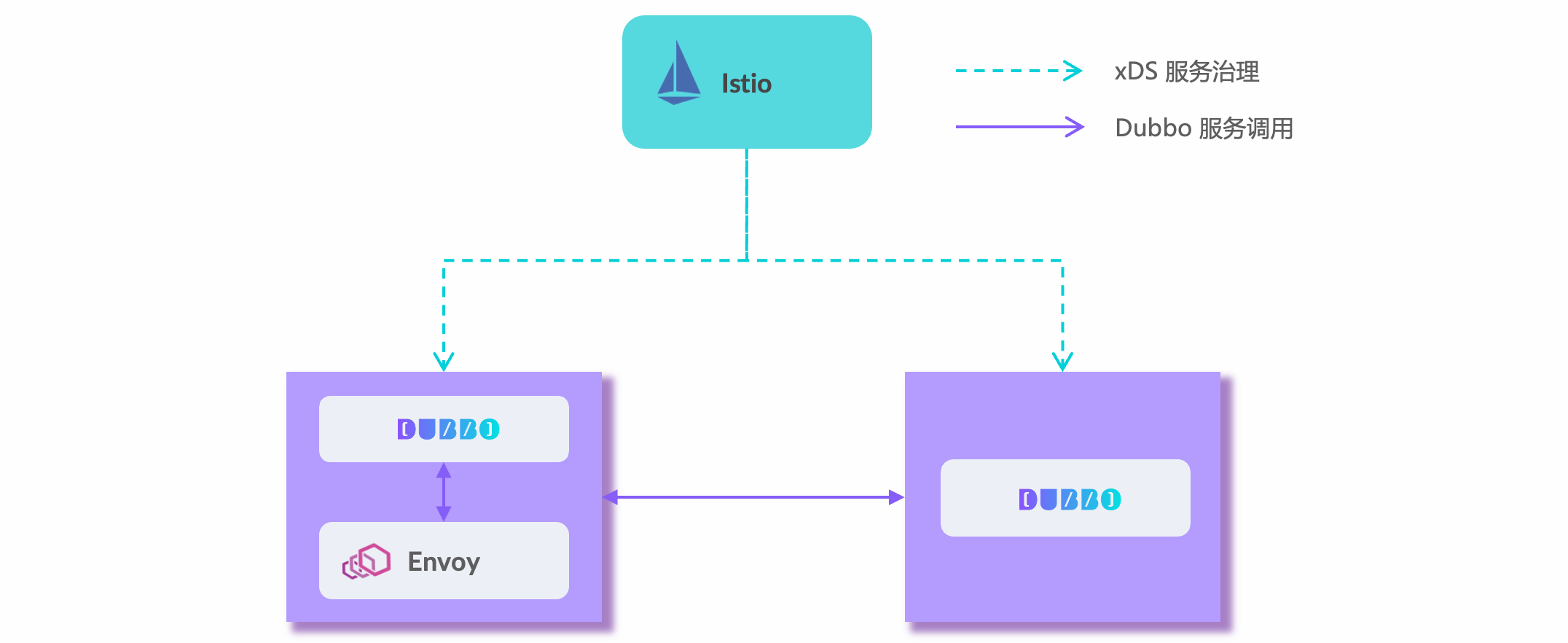
View Dubbo Mesh design details here
Deployment Architecture
This section focuses on describing the Dubbo deployment architecture in the traditional mode. The deployment architecture in the cloud-native background will change, mainly reflected in the fact that the infrastructure (Kubernetes, Service Mesh, etc.) will take on more responsibilities. The responsibilities of centralized components such as registration center, metadata center, configuration center, etc. are integrated, and operation and maintenance become simpler, but by emphasizing these centralized components, it is easier for us to understand the working principle of Dubbo.
As a micro-service framework, Dubbo sdk is deployed in each location of the distributed cluster along with the micro-service components. In order to realize the cooperation between various micro-service components in a distributed environment, Dubbo defines some centralized components, including:
- Registry. Coordinate address registration and discovery between Consumer and Provider
- Configuration center.
- Store the global configuration of the Dubbo startup phase to ensure cross-environment sharing and global consistency of the configuration
- Responsible for the storage and push of service governance rules (routing rules, dynamic configuration, etc.).
- Metadata Center.
- Receive the service interface metadata reported by the Provider, and provide operation and maintenance capabilities for Admin and other consoles (such as service testing, interface documents, etc.)
- As a supplement to the service discovery mechanism, it provides the synchronization capability of additional interface/method level configuration information, which is equivalent to the additional extension of the registration center
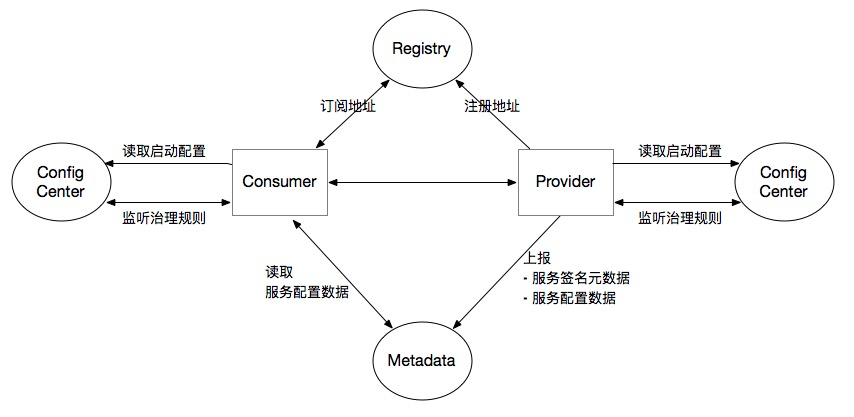
The above figure completely describes the interaction process between Dubbo microservice components and each center.
The above three centers are not a necessary condition for running Dubbo. Users can decide to enable only one or more of them according to their own business conditions to simplify deployment. Typically, all users will be registered with an independent Start Dubbo service development, and the configuration center and metadata center will be gradually introduced on demand during the evolution of microservices.
Registry
The registration center plays a very important role, and it carries the responsibilities of service registration and service discovery. Currently Dubbo supports service discovery and service registration at the following two granularities, namely interface level and application level, and the registration center can be deployed on demand:
In the traditional Dubbo SDK usage posture, if you only provide RPC services in direct connection mode, you do not need to deploy a registration center.
Regardless of the interface level or the application level, if Dubbo SDK itself is required for service registration and service discovery, you can choose to deploy a registration center and integrate the corresponding registration center in Dubbo.
In the Dubbo + Mesh scenario, with the weakening of Dubbo service registration capabilities, the registration center in Dubbo is no longer a must, and its responsibilities are beginning to be replaced by the control plane. If the Dubbo + Mesh deployment method is adopted, whether it is The mesh method of ThinSDK or the mesh method of Proxyless no longer requires independent deployment of the registration center.
The registration center does not depend on the configuration center and metadata center, as shown in the following figure:
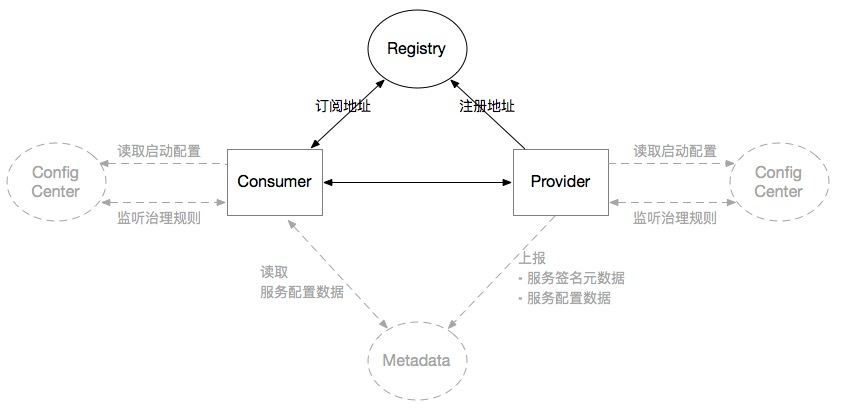
The configuration center and metadata center are not deployed in the figure. In Dubbo, the instance of the registration center will be used as the configuration center and metadata center at the same time by default. This is the default behavior of Dubbo. If you really do not need the capabilities of the configuration center or metadata center , which can be turned off in the configuration. There are two configurations in the configuration of the registration center, namely use-as-config-center and use-as-metadata-center. Just set the configuration to false.
Metadata Center
The metadata center is supported in version 2.7.x. As application-level service registration and service discovery are implemented in Dubbo, the metadata center becomes more and more important. The metadata center will need to be deployed in the following situations:
- For an application service originally built with the old version of Dubbo, when migrating to Dubbo 3, Dubbo 3 will need a metadata center to maintain the mapping relationship between RPC services and applications (that is, the mapping relationship between interfaces and applications), because if Application-level service discovery and service registration are adopted, and the data organization form of the “application-instance list” structure will be adopted in the registration center, which is no longer the data organization form of the previous “interface-instance list” structure. When the application services that use interface-level service registration and service discovery are migrated to the application level, the corresponding relationship between the interface and the application cannot be obtained, so that the instance list information cannot be obtained from the registration center. Therefore, in order to be compatible with this scenario, Dubbo is in When the Provider side starts, it will store the mapping relationship between the interface and the application in the metadata center.
- In order to allow the registration center to focus more on address discovery and push capabilities and reduce the burden on the registration center, the metadata center carries all service metadata, a large number of interface/method level configuration information, etc., regardless of interface granularity or application granularity Service discovery and registration, and the metadata center all play an important role.
If you have the above two requirements, you can choose to deploy the metadata center and integrate the metadata center through Dubbo configuration.
The metadata center does not depend on the registration center and configuration center, and users can freely choose whether to integrate and deploy the metadata center, as shown in the following figure:
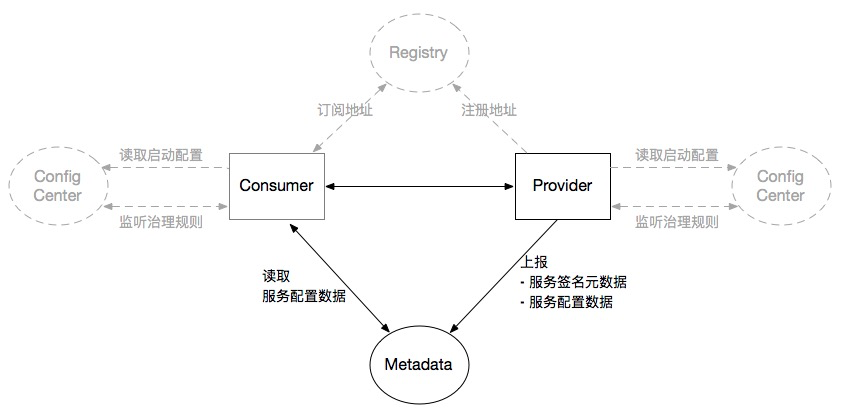
There is no configuration center in this figure, which means that the ability to manage configuration globally may not be required. There is no registration center in the figure, which means that the Dubbo mesh solution may be adopted, or service registration may not be required, and only receive service calls in direct connection mode.
Configuration Center
The configuration center is different from the other two centers. It has nothing to do with the interface level or the application level. It has no corresponding relationship with the interface. It is only related to the configuration data. Even if the registration center and metadata center are not deployed, the configuration center can be directly accessed. into the Dubbo application service. In the entire deployment architecture, instances in the entire cluster (whether they are Providers or Consumers) will share the configuration in the configuration center cluster, as shown in the following figure:
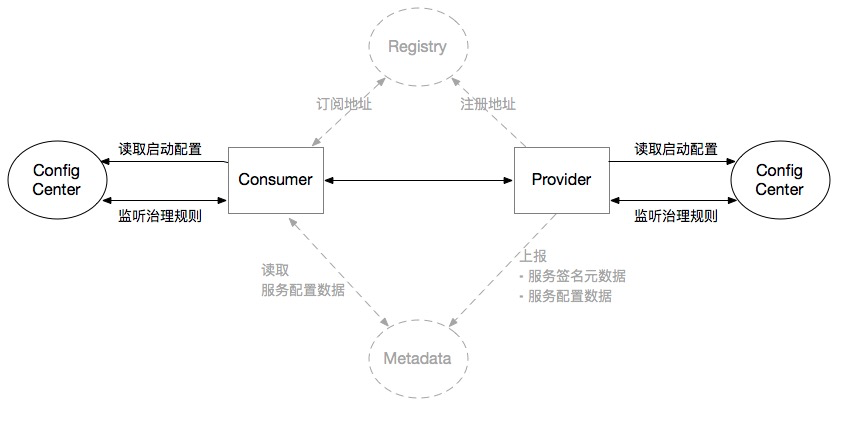
There is no registration center in the figure, which means that the Dubbo mesh solution may be adopted, or service registration may not be required, and only receive service calls in direct connection mode.
There is no metadata center in this figure, which means that Consumer can obtain service metadata from the MetadataService exposed by Provider, so as to realize RPC call
Guarantee the high-availability deployment architecture of the three centers
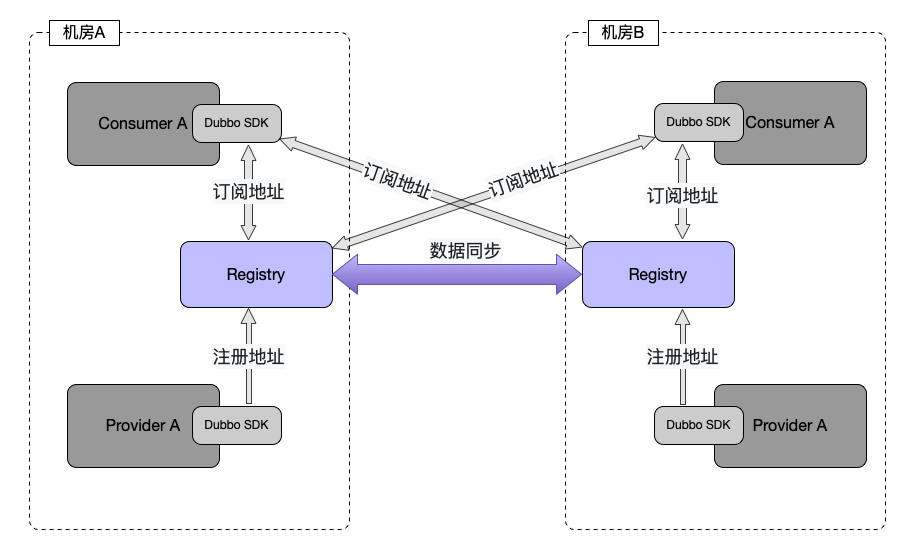
Although the three major centers are no longer necessary for Dubbo application services, in a real production environment, once the three major centers have been integrated and deployed, the three major centers will still face availability issues. Dubbo needs to support the three major centers High availability solution. Dubbo supports multiple registration centers, multiple data centers, and multiple configuration centers to meet the needs of deployment architecture models such as multi-active in the same city, three centers in two places, and multi-active in different places.
Dubbo SDK supports Multiple mode for all three centers.
Multiple registries: Dubbo supports multiple registries, that is, an interface or an application can be registered in multiple registries, such as ZK clusters and Nacos clusters, and consumers can also subscribe from multiple registries Service address information for service discovery. By supporting multiple registration centers, it is ensured that one of the registration center clusters can be switched to another registration center cluster when it is unavailable, so that services can be provided normally and service calls can be initiated. This can also satisfy the registration center to adapt to various high-availability deployment architecture modes in deployment.
Multiple configuration centers: Dubbo supports multiple configuration centers to ensure that when a configuration center cluster becomes unavailable, it can switch to another configuration center cluster to ensure that the global configuration, routing rules, and other information can be obtained from the configuration center normally. This can also satisfy the configuration center to adapt to various high-availability deployment architecture modes in deployment.
Multiple data centers: Dubbo supports multiple data centers: it is used to deal with disaster recovery and other situations where a metadata center cluster is unavailable. At this time, you can switch to another metadata center cluster to ensure that the metadata center can normally provide relevant service elements. Data management capabilities.
Taking the registration center as an example, the following is a schematic diagram of the deployment architecture of a multi-active scenario: