Address Synchronization
By following these steps, you can easily master how to develop Dubbo services that comply with the Service Mesh architecture and deploy them to Kubernetes while integrating with Istio’s traffic management system. Here you can view the complete example source code.
1 Overall Goal
- Deploy Dubbo applications to Kubernetes
- Istio automatically injects Envoy and implements traffic interception
- Implement traffic governance based on Istio rules
2 Basic Process and Working Principle
This example demonstrates how to deploy applications developed with Dubbo under the Istio framework to achieve automatic proxying of Dubbo services by Envoy. The overall architecture of the example is shown in the figure below.
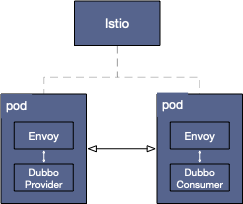
The steps needed to complete the example are as follows:
- Create a Dubbo application (dubbo-samples-mesh-k8s)
- Build the container image and push it to the image repository (official image for this example)
- Deploy the Dubbo Provider and Dubbo Consumer to Kubernetes and verify that the Envoy proxy has been successfully injected
- Verify that Envoy discovers the service address, properly intercepts RPC traffic, and implements load balancing
- Implement proportional traffic forwarding based on Istio VirtualService
3 Detailed Steps
3.1 Environment Requirements
Please ensure the following environments are installed locally to provide container runtime, Kubernetes cluster, and access tools:
Start the local Kubernetes cluster with the following command:
minikube start
Check that the cluster is running properly and that kubectl is bound to the default local cluster:
kubectl cluster-info
3.2 Create a Separate Namespace and Enable Automatic Injection
Run the following commands to create a separate Namespace dubbo-demo for the example project and enable sidecar automatic injection.
# Initialize namespace
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/apache/dubbo-samples/master/3-extensions/registry/dubbo-samples-mesh-k8s/deploy/Namespace.yml
# Switch namespace
kubens dubbo-demo
# Enable automatic injection for dubbo-demo
kubectl label namespace dubbo-demo istio-injection=enabled
3.3 Deploy to Kubernetes
3.3.1 Deploy Provider
# Deploy Service
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/apache/dubbo-samples/master/3-extensions/registry/dubbo-samples-mesh-k8s/deploy/provider/Service.yml
# Deploy Deployment
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/apache/dubbo-samples/master/3-extensions/registry/dubbo-samples-mesh-k8s/deploy/provider/Deployment.yml
The above commands create a Service named dubbo-samples-mesh-provider. Note that the service name here is the same as the Dubbo application name in the project.
Next, the Deployment deploys a pod instance with 2 replicas, completing the Provider startup.
You can check the startup logs with the following commands:
# View pod list
kubectl get pods -l app=dubbo-samples-mesh-provider
# View pod deployment logs
kubectl logs your-pod-id
At this point, there should be a Dubbo provider container instance in the pod, along with an Envoy Sidecar container instance.
3.3.2 Deploy Consumer
# Deploy Service
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/apache/dubbo-samples/master/3-extensions/registry/dubbo-samples-mesh-k8s/deploy/consumer/Service.yml
# Deploy Deployment
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/apache/dubbo-samples/master/3-extensions/registry/dubbo-samples-mesh-k8s/deploy/consumer/Deployment.yml
Deploying the consumer is the same as the provider, with the K8S Service and Dubbo consumer application name (defined in dubbo.properties) kept consistent: dubbo.application.name=dubbo-samples-mesh-consumer.
The Dubbo Consumer service declaration also specifies the provider’s service (application) name as
@DubboReference(version = "1.0.0", providedBy = "dubbo-samples-mesh-provider", lazy = true)
3.4 Check Normal Communication Between Provider and Consumer
After executing step 3.3, check the startup logs to see if the consumer has finished consuming the provider service.
# View pod list
kubectl get pods -l app=dubbo-samples-mesh-consumer
# View pod deployment logs
kubectl logs your-pod-id
# View pod istio-proxy logs
kubectl logs your-pod-id -c istio-proxy
You can see that the consumer pod log outputs as follows (Triple protocol is load balanced by Envoy):
==================== dubbo invoke 0 end ====================
[10/08/22 07:07:36:036 UTC] main INFO action.GreetingServiceConsumer: consumer Unary reply <-message: "hello,service mesh, response from provider-v1: 172.18.96.22:50052, client: 172.18.96.22, local: dubbo-samples-mesh-provider, remote: null, isProviderSide: true"
==================== dubbo invoke 1 end ====================
[10/08/22 07:07:42:042 UTC] main INFO action.GreetingServiceConsumer: consumer Unary reply <-message: "hello,service mesh, response from provider-v1: 172.18.96.18:50052, client: 172.18.96.18, local: dubbo-samples-mesh-provider, remote: null, isProviderSide: true"
The logs output from the consumer istio-proxy is as follows:
[2022-07-15T05:35:14.418Z] "POST /org.apache.dubbo.samples.Greeter/greet HTTP/2" 200
- via_upstream - "-" 19 160 2 1 "-" "-" "6b8a5a03-5783-98bf-9bee-f93ea6e3d68e"
"dubbo-samples-mesh-provider:50052" "172.17.0.4:50052"
outbound|50052||dubbo-samples-mesh-provider.dubbo-demo.svc.cluster.local 172.17.0.7:52768 10.101.172.129:50052 172.17.0.7:38488 - default
You can see that the provider pod logs output as follows:
[10/08/22 07:08:47:047 UTC] tri-protocol-50052-thread-8 INFO impl.GreeterImpl: Server test dubbo tri mesh received greet request name: "service mesh"
[10/08/22 07:08:57:057 UTC] tri-protocol-50052-thread-9 INFO impl.GreeterImpl: Server test dubbo tri mesh received greet request name: "service mesh"
The logs output from the provider istio-proxy is as follows:
[2022-07-15T05:25:34.061Z] "POST /org.apache.dubbo.samples.Greeter/greet HTTP/2" 200
- via_upstream - "-" 19 162 1 1 "-" "-" "201e6976-da10-96e1-8da7-ad032e58db47"
"dubbo-samples-mesh-provider:50052" "172.17.0.10:50052"
inbound|50052|| 127.0.0.6:47013 172.17.0.10:50052 172.17.0.7:60244
outbound_.50052_._.dubbo-samples-mesh-provider.dubbo-demo.svc.cluster.local default
3.5 Traffic Management - VirtualService for Proportional Traffic Forwarding
Deploy the v2 version of the demo provider:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/apache/dubbo-samples/master/3-extensions/registry/dubbo-samples-mesh-k8s/deploy/provider/Deployment-v2.yml
Set up VirtualService and DestinationRule, observe traffic being directed to provider v1 and provider v2 versions in a ratio of 4:1:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/apache/dubbo-samples/master/3-extensions/registry/dubbo-samples-mesh-k8s/deploy/traffic/virtual-service.yml
From the consumer’s log output, observe the traffic distribution effect as shown in the figure below:
==================== dubbo invoke 100 end ====================
[10/08/22 07:15:58:058 UTC] main INFO action.GreetingServiceConsumer: consumer Unary reply <-message: "hello,service mesh, response from provider-v1: 172.18.96.18:50052, client: 172.18.96.18, local: dubbo-samples-mesh-provider, remote: null, isProviderSide: true"
==================== dubbo invoke 101 end ====================
[10/08/22 07:16:03:003 UTC] main INFO action.GreetingServiceConsumer: consumer Unary reply <-message: "hello,service mesh, response from provider-v1: 172.18.96.22:50052, client: 172.18.96.22, local: dubbo-samples-mesh-provider, remote: null, isProviderSide: true"
==================== dubbo invoke 102 end ====================
[10/08/22 07:16:08:008 UTC] main INFO action.GreetingServiceConsumer: consumer Unary reply <-message: "hello,service mesh, response from provider-v1: 172.18.96.18:50052, client: 172.18.96.18, local: dubbo-samples-mesh-provider, remote: null, isProviderSide: true"
==================== dubbo invoke 103 end ====================
[10/08/22 07:16:13:013 UTC] main INFO action.GreetingServiceConsumer: consumer Unary reply <-message: "hello,service mesh, response from provider-v2: 172.18.96.6:50052, client: 172.18.96.6, local: dubbo-samples-mesh-provider, remote: null, isProviderSide: true"
==================== dubbo invoke 104 end ====================
[10/08/22 07:16:18:018 UTC] main INFO action.GreetingServiceConsumer: consumer Unary reply <-message: "hello,service mesh, response from provider-v1: 172.18.96.22:50052, client: 172.18.96.22, local: dubbo-samples-mesh-provider, remote: null, isProviderSide: true"
==================== dubbo invoke 105 end ====================
[10/08/22 07:16:24:024 UTC] main INFO action.GreetingServiceConsumer: consumer Unary reply <-message: "hello,service mesh, response from provider-v1: 172.18.96.18:50052, client: 172.18.96.18, local: dubbo-samples-mesh-provider, remote: null, isProviderSide: true"
==================== dubbo invoke 106 end ====================
[10/08/22 07:16:29:029 UTC] main INFO action.GreetingServiceConsumer: consumer Unary reply <-message: "hello,service mesh, response from provider-v1: 172.18.96.22:50052, client: 172.18.96.22, local: dubbo-samples-mesh-provider, remote: null, isProviderSide: true"
==================== dubbo invoke 107 end ====================
[10/08/22 07:16:34:034 UTC] main INFO action.GreetingServiceConsumer: consumer Unary reply <-message: "hello,service mesh, response from provider-v1: 172.18.96.18:50052, client: 172.18.96.18, local: dubbo-samples-mesh-provider, remote: null, isProviderSide: true"
==================== dubbo invoke 108 end ====================
[10/08/22 07:16:39:039 UTC] main INFO action.GreetingServiceConsumer: consumer Unary reply <-message: "hello,service mesh, response from provider-v1: 172.18.96.22:50052, client: 172.18.96.22, local: dubbo-samples-mesh-provider, remote: null, isProviderSide: true"
==================== dubbo invoke 109 end ====================
[10/08/22 07:16:44:044 UTC] main INFO action.GreetingServiceConsumer: consumer Unary reply <-message: "hello,service mesh, response from provider-v1: 172.18.96.18:50052, client: 172.18.96.18, local: dubbo-samples-mesh-provider, remote: null, isProviderSide: true"
3.6 View Dashboard
Refer to the Istio website for how to start the dashboard.
4 Modify Example
- Modifying the example is not a mandatory step. This section is prepared for readers who want to adjust the code and observe the deployment effects.
- Note that the project source code storage path must be in English; otherwise, protobuf compilation will fail.
Modify Dubbo Provider configuration in dubbo-provider.properties.
# provider
dubbo.application.name=dubbo-samples-mesh-provider
dubbo.application.metadataServicePort=20885
dubbo.registry.address=N/A
dubbo.protocol.name=tri
dubbo.protocol.port=50052
dubbo.application.qosEnable=true
# To allow Kubernetes cluster to access the probe normally, QOS must be enabled for remote access. This operation may pose security risks; please assess carefully before enabling.
dubbo.application.qosAcceptForeignIp=true
Modify Dubbo Consumer configuration in dubbo-consumer.properties.
# consumer
dubbo.application.name=dubbo-samples-mesh-consumer
dubbo.application.metadataServicePort=20885
dubbo.registry.address=N/A
dubbo.protocol.name=tri
dubbo.protocol.port=20880
dubbo.consumer.timeout=30000
dubbo.application.qosEnable=true
# To allow Kubernetes cluster to access the probe normally, QOS must be enabled for remote access. This operation may pose security risks; please assess carefully before enabling.
dubbo.application.qosAcceptForeignIp=true
# Mark to enable mesh sidecar proxy mode
dubbo.consumer.meshEnable=true
After completing code modifications, package the image using the Dockerfile provided by the project.
# Package and push the image
mvn compile jib:build
The Jib plugin will automatically package and publish the image. Note that for local development, change the organization
apache/dubbo-demoin the configuration of the Jib plugin to an organization you have permission for (including other Kubernetes manifests also need to be modified to ensure that the Kubernetes deployment is the customized image). If you encounter Jib plugin authentication issues, refer to the relevant link for configuring Docker registry credentials. You can directly specify in the command linemvn compile jib:build -Djib.to.auth.username=x -Djib.to.auth.password=x -Djib.from.auth.username=x -Djib.from.auth.username=x, or use docker-credential-helper.
5 Common Commands
# dump current Envoy configs
kubectl exec -it ${your pod id} -c istio-proxy curl http://127.0.0.1:15000/config_dump > config_dump
# Enter istio-proxy container
kubectl exec -it ${your pod id} -c istio-proxy -- /bin/bash
# View container logs
kubectl logs ${your pod id} -n ${your namespace}
kubectl logs ${your pod id} -n ${your namespace} -c istio-proxy
# Enable automatic sidecar injection
kubectl label namespace ${your namespace} istio-injection=enabled --overwrite
# Disable automatic sidecar injection
kubectl label namespace ${your namespace} istio-injection=disabled --overwrite
6 Precautions
- In this example, both the producer and consumer belong to the same namespace; if you need to call providers from different namespaces, you need to configure as follows (dubbo version >= 3.1.2):
Annotation method:
@DubboReference(providedBy = "istio-demo-dubbo-producer", providerPort = 20885, providerNamespace = "istio-demo")
XML method
<dubbo:reference id="demoService" check="true"
interface="org.apache.dubbo.samples.basic.api.DemoService"
provider-port="20885"
provided-by="istio-dubbo-producer"
provider-namespace="istio-demo"/>