This article is more than one year old. Older articles may contain outdated content. Check that the information in the page has not become incorrect since its publication.
How to proxy Dubbo service in Apache ShenYu Gateway
Dubbo service through the Apache ShenYu gateway. The main content includes a simple example to core call flow analysis and a summary of the design principles.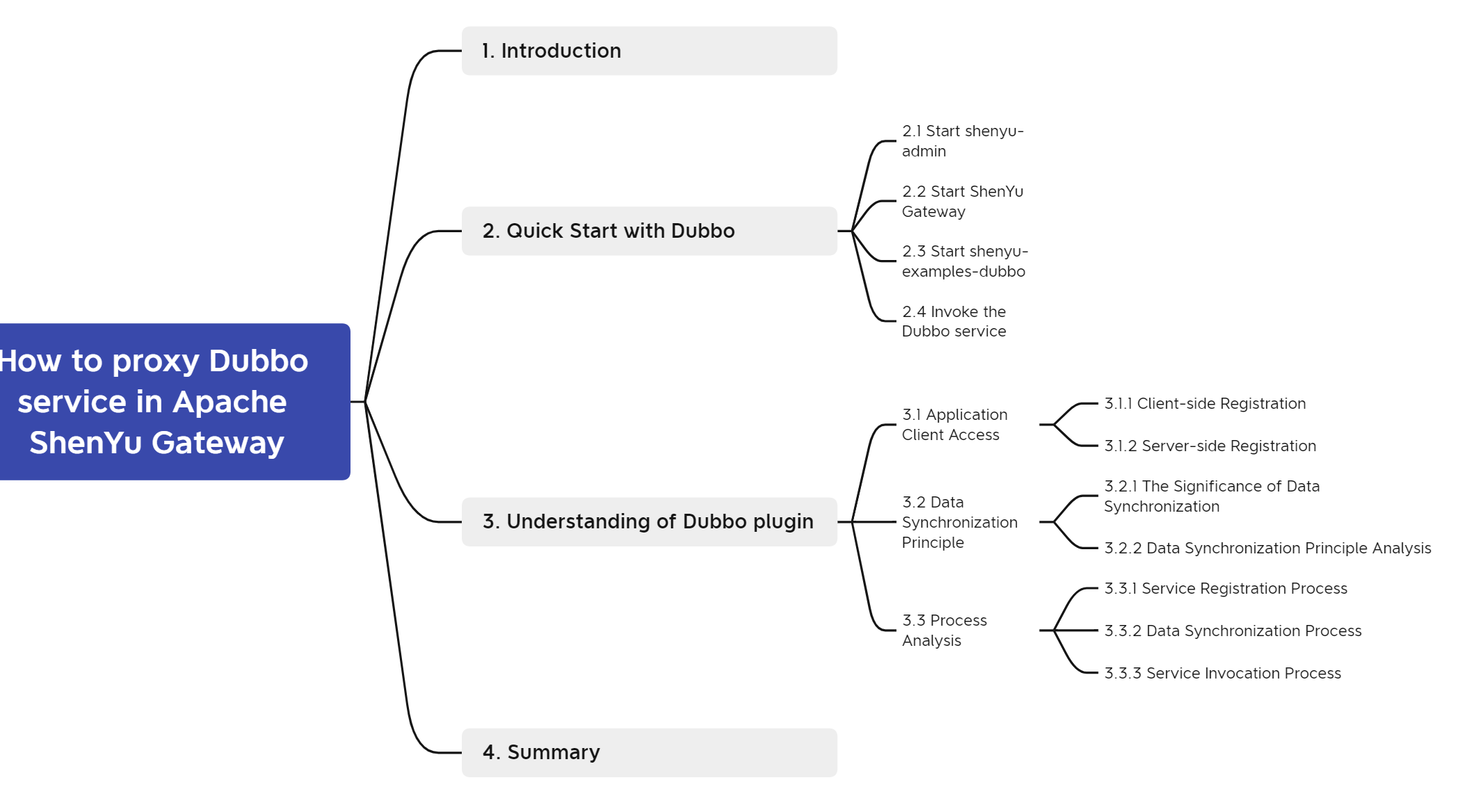
1. Introduction
- Apache ShenYu
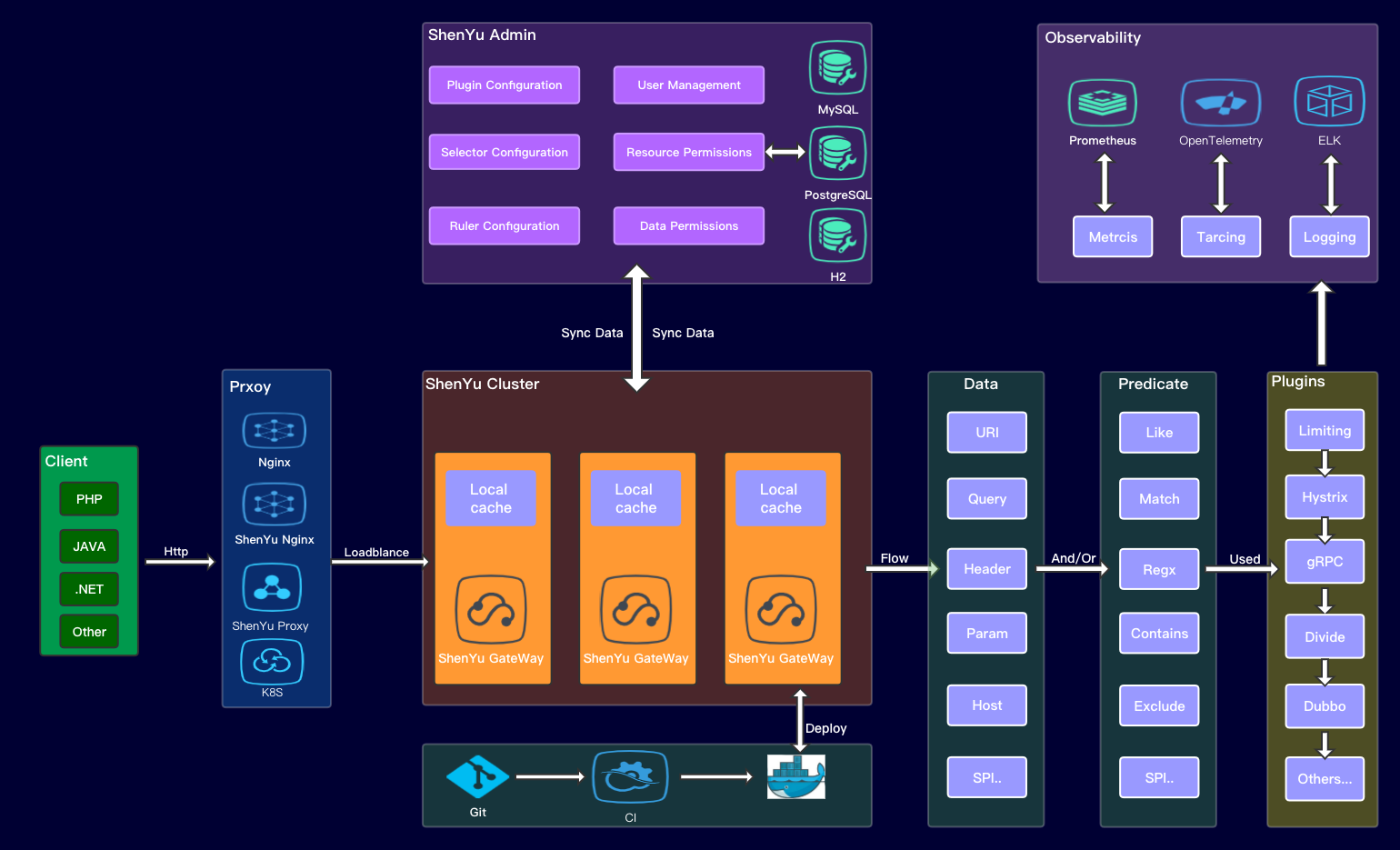
Apache ShenYu(Incubating) is an asynchronous, high-performance, cross-language, responsive API gateway. Compatible with a variety of mainstream framework systems, support for hot-plugging, users can customize the development to meet the current and future needs of users in a variety of scenarios, experienced large-scale scenarios hammered.
In May 2021, ShenYu was donated to the Apache Software Foundation, and the Apache Foundation voted unanimously to enter the incubator.
- Apache Dubbo
Apache Dubbo is a microservice development framework that provides two key capabilities, RPC communication and microservice governance. This means that microservices developed with Dubbo will have the ability to discover and communicate with each other remotely, and take advantage of the rich service governance capabilities provided by Dubbo to achieve service governance requirements such as service discovery, load balancing, traffic scheduling, and so on. At the same time Dubbo is highly scalable, users can customize their own implementation at almost any point to change the default behavior of the framework to meet their business needs.
2. Quick Start with Dubbo
This section describes how to connect the Dubbo service to the Shenyu gateway. You can find the [sample code] for this section directly under the project (https://github.com/apache/shenyu/tree/master/shenyu-examples/shenyu-examples-dubbo -examples-dubbo/shenyu-examples-apache-dubbo-service).
2.1 Start shenyu-admin
shenyu-admin is the Apache ShenYu backend management system, there are various ways to start it, this article is started by [local deployment](https://shenyu.apache.org/docs/deployment/deployment-local) way. After successful startup, you need to set the dubbo plugin to be on and set your registered address in the base configuration ->Plugin Management’, please make sure the registration center has been opened.
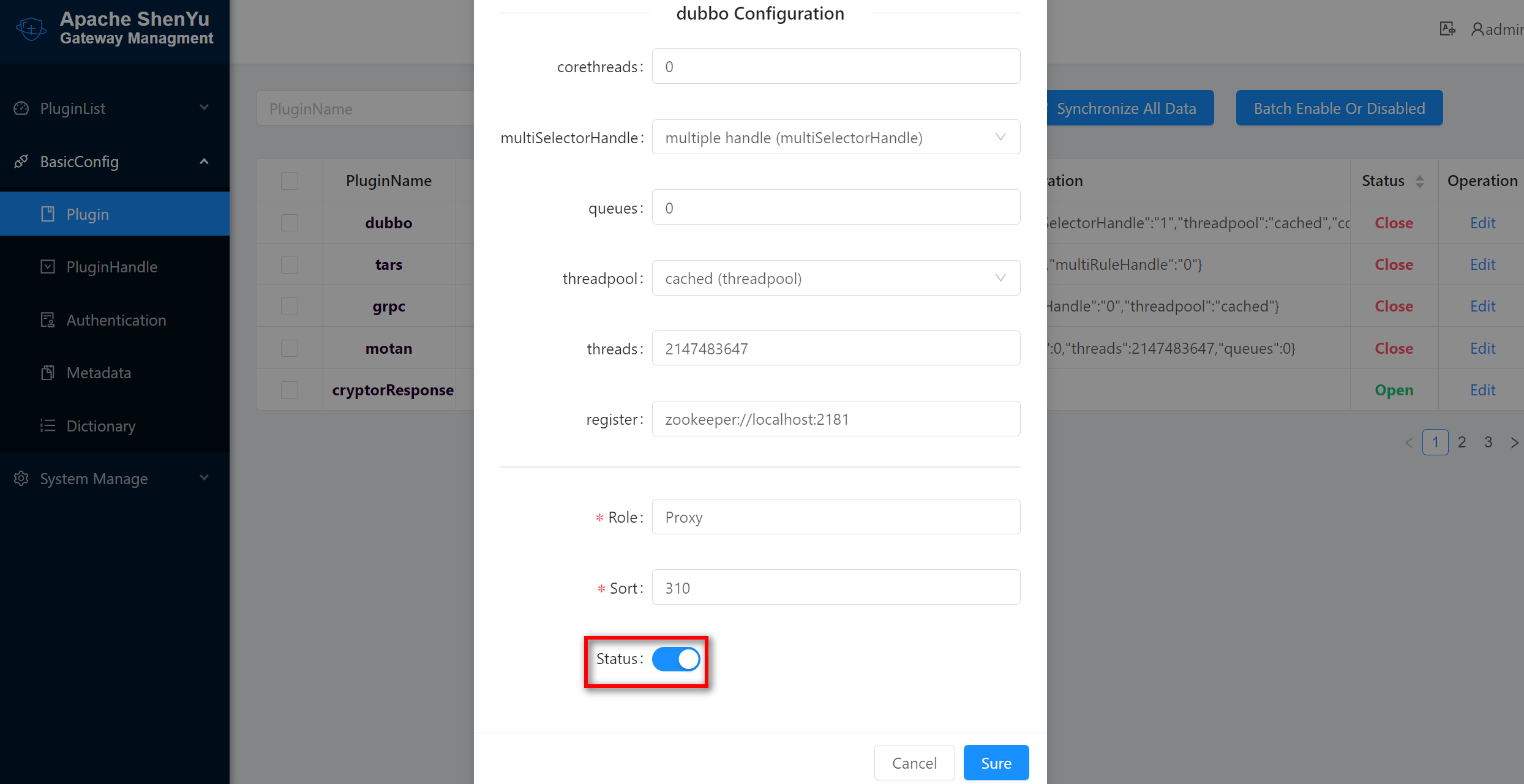
2.2 Start ShenYu Gateway
Here it is started by way of source and runs directly shenyu-bootstrap in shenyu-bootstrap. ShenyuBootstrapApplication`.
Make sure the gateway has introduced the relevant dependencies before starting. If the client is apache dubbo and the registry uses zookeeper, please refer to the following configuration.
<!-- apache shenyu apache dubbo plugin start-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shenyu</groupId>
<artifactId>shenyu-spring-boot-starter-plugin-apache-dubbo</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo</artifactId>
<version>2.7.5</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Dubbo zookeeper registry dependency start -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-client</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-framework</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-recipes</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Dubbo zookeeper registry dependency end -->
<!-- apache dubbo plugin end-->
2.3 Start shenyu-examples-dubbo
Take the example provided on the official website shenyu-examples-dubbo. Suppose the dubbo service is defined as follows.
<beans /* ...... * />
<dubbo:application name="test-dubbo-service"/>
<dubbo:registry address="${dubbo.registry.address}"/>
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="20888"/>
<dubbo:service timeout="10000" interface="org.apache.shenyu.examples.dubbo.api.service.DubboTestService" ref="dubboTestService"/>
</beans>
Declare the application service name, register the center address, use the dubbo protocol, declare the service interface, and the corresponding interface implementation class.
/**
* DubboTestServiceImpl.
*/
@Service("dubboTestService")
public class DubboTestServiceImpl implements DubboTestService {
@Override
@ShenyuDubboClient(path = "/findById", desc = "Query by Id")
public DubboTest findById(final String id) {
return new DubboTest(id, "hello world shenyu Apache, findById");
}
//......
}
In the interface implementation class, use the annotation @ShenyuDubboClient to register the service with shenyu-admin.
Configuration information in the configuration file application.yml.
server:
port: 8011
address: 0.0.0.0
servlet:
context-path: /
spring:
main:
allow-bean-definition-overriding: true
dubbo:
registry:
address: zookeeper://localhost:2181 # The registry used by dubbo
shenyu:
register:
registerType: http #Registration Method
serverLists: http://localhost:9095 #Registration Address
props:
username: admin
password: 123456
client:
dubbo:
props:
contextPath: /dubbo
appName: dubbo
In the configuration file, declare the registry address used by dubbo. The dubbo service registers with shenyu-admin, using the method http, and the registration address is http://localhost:9095.
See [Application Client Access](https://shenyu.apache.org/docs/design/register-center-design/) for more information on the use of the registration method.
2.4 Invoke the Dubbo service
The shenyu-examples-dubbo project will automatically register the interface methods annotated with @ShenyuDubboClient to the gateway after it is successfully started.
Open Plugins List -> Proxy -> dubbo to see the list of plugin rules configuration.
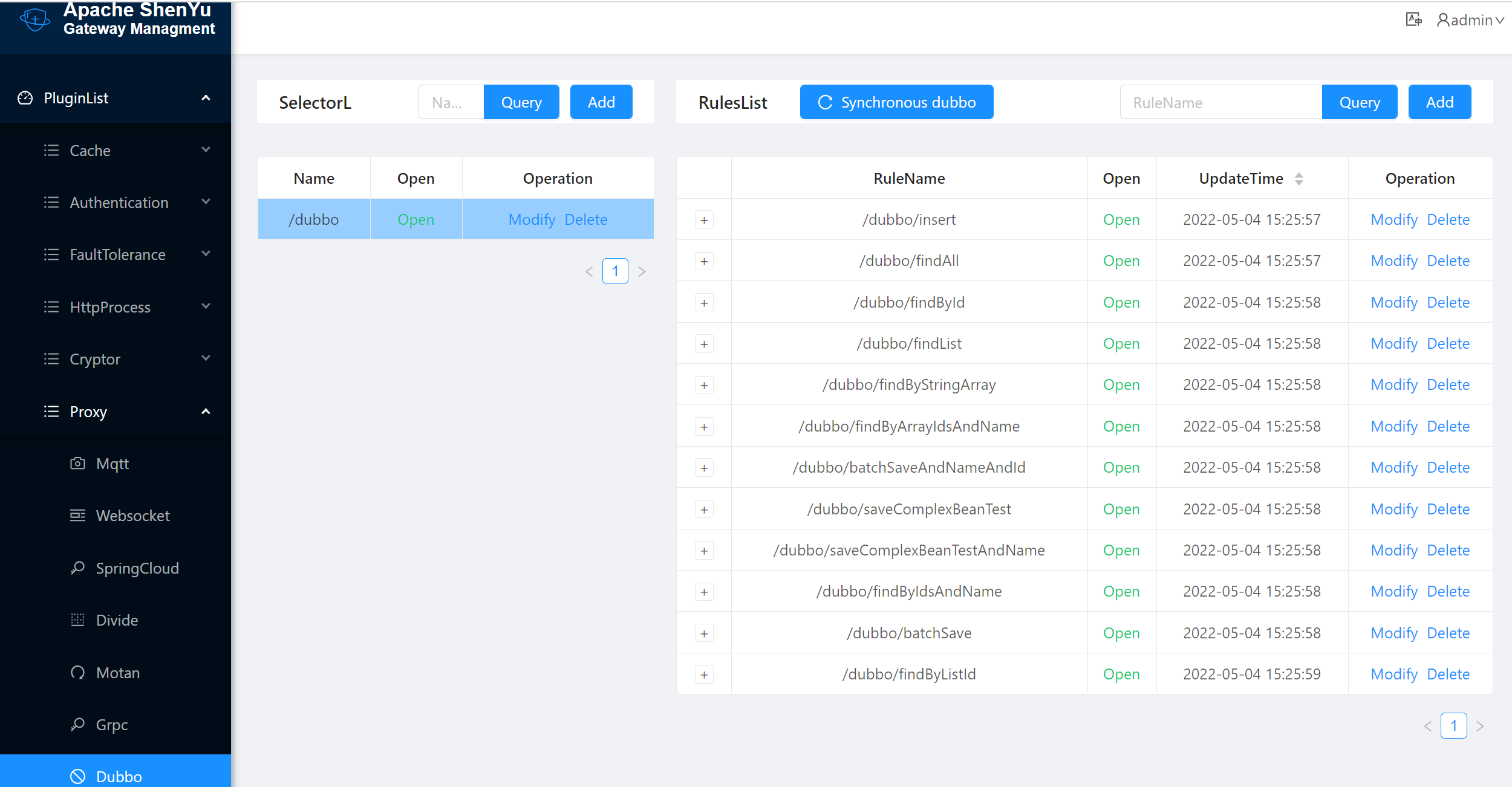
Information on the selectors for successful registration.
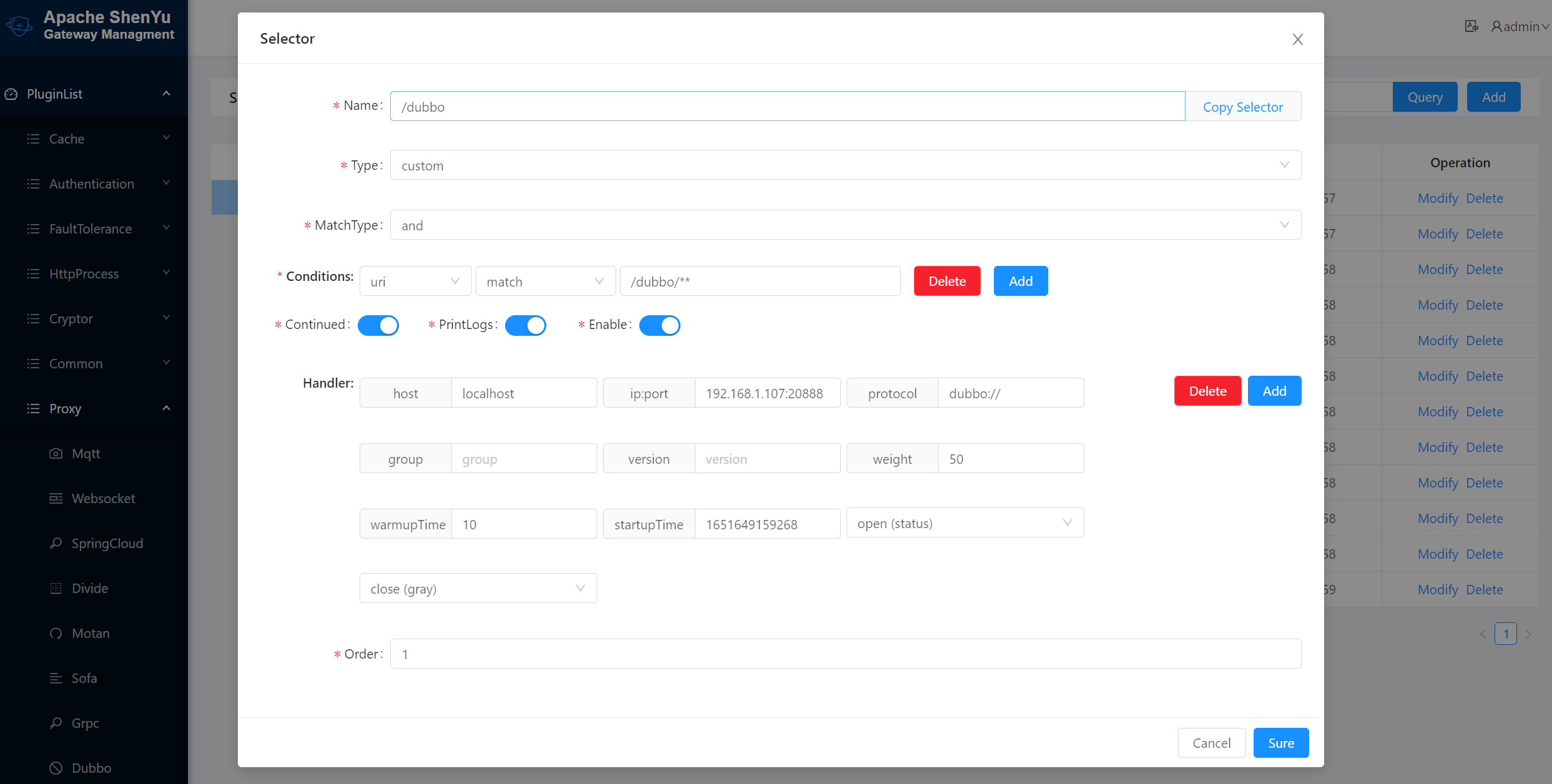
Information on the rules for successful registration.
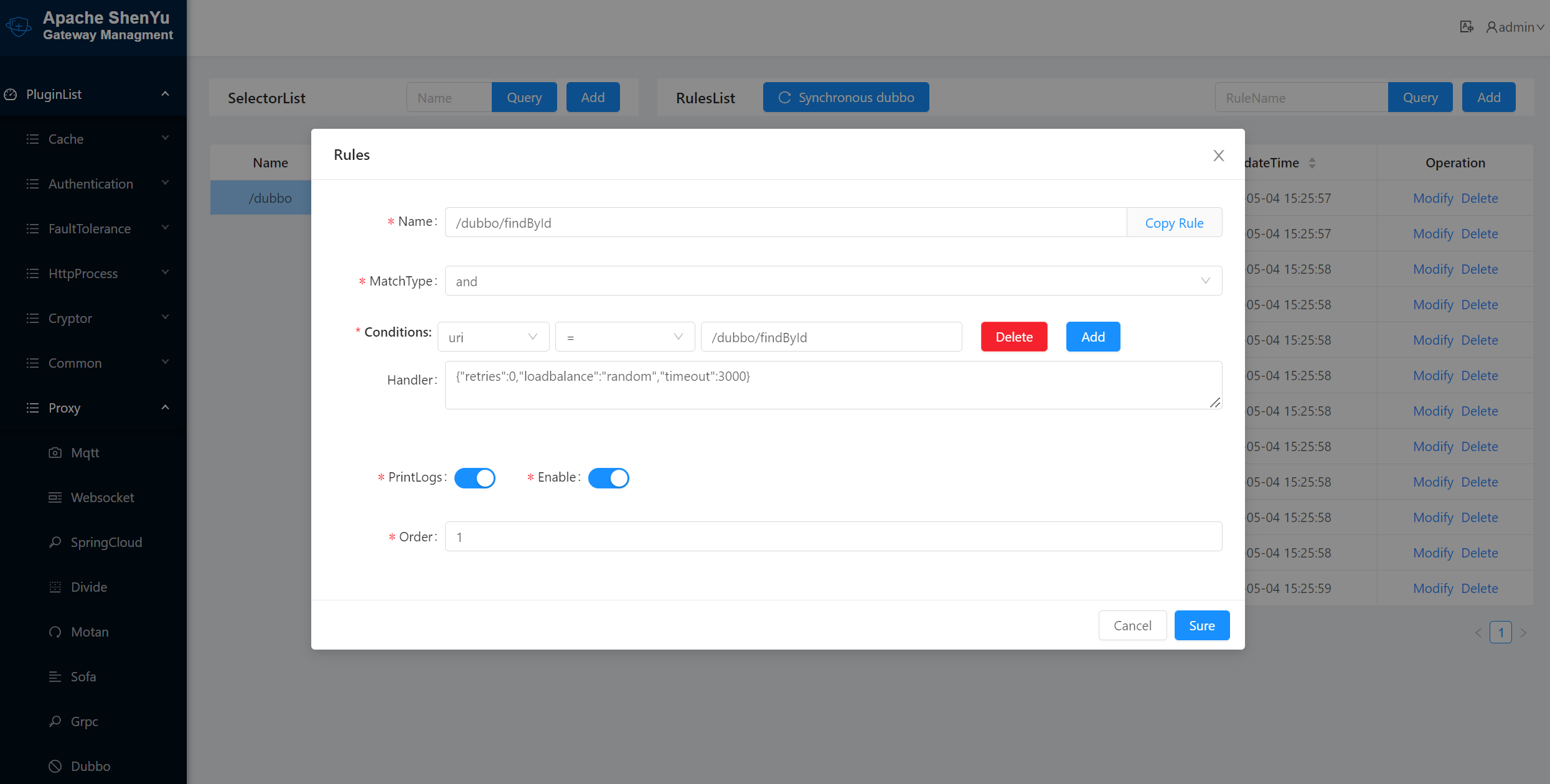
Selectors and rules are the soul of the
Apache ShenYugateway. Mastering it well, you can manage any traffic. Corresponding to the matching conditions (conditions) inside the selectors and rules, we can handle various complex scenarios according to different traffic filtering rules. Traffic filtering can get data fromHeader,URI,Query,Cookieand so on Http requests.Then you can use
Match,=,Regex,Groovy,Excludeand other matching methods to match the data you expect. Multi-group match additions can use theAnd/Ormatching strategy.See:
[Selector and Rule Management](https://shenyu.apache.org/docs/user-guide/admin-usage/selector-and-rule)for details and usage.
Initiate a GET request to invoke the dubbo service through the ShenYu gateway.
GET http://localhost:9195/dubbo/findById?id=100
Accept: application/json
After a successful response, the result is as follows.
{
"name": "hello world shenyu Apache, findById",
"id": "100"
}
At this point, you can successfully access the dubbo service via http requests. The ShenYu gateway converts the http protocol to the dubbo protocol via the shenyu-plugin-dubbo module.
3. Understanding of Dubbo plugin
During the process of running the above demo, are there any questions about
- How does the
dubboservice register withshenyu-admin? - How does
shenyu-adminsynchronize data to theShenYugateway? - How does the
DubboPluginconvert thehttpprotocol to thedubboprotocol?
With these questions in mind, let’s dive into understanding the dubbo plugin.
3.1 Application Client Access
Application client access refers to accessing microservices to the Apache ShenYu gateway, which currently supports access to Http, Dubbo, Spring Cloud, gRPC, Motan, Sofa, Tars and other protocols.
Accessing application clients to the Apache ShenYu gateway is achieved through the registry, which involves client-side registration and server-side synchronization of data. The registry supports Http, Zookeeper, Etcd, Consul and Nacos. The default is to register by Http.
Please refer to [Client Access Configuration](https://shenyu.apache.org/docs/user-guide/register-center-access) for client access related configuration.
3.1.1 Client-side Registration
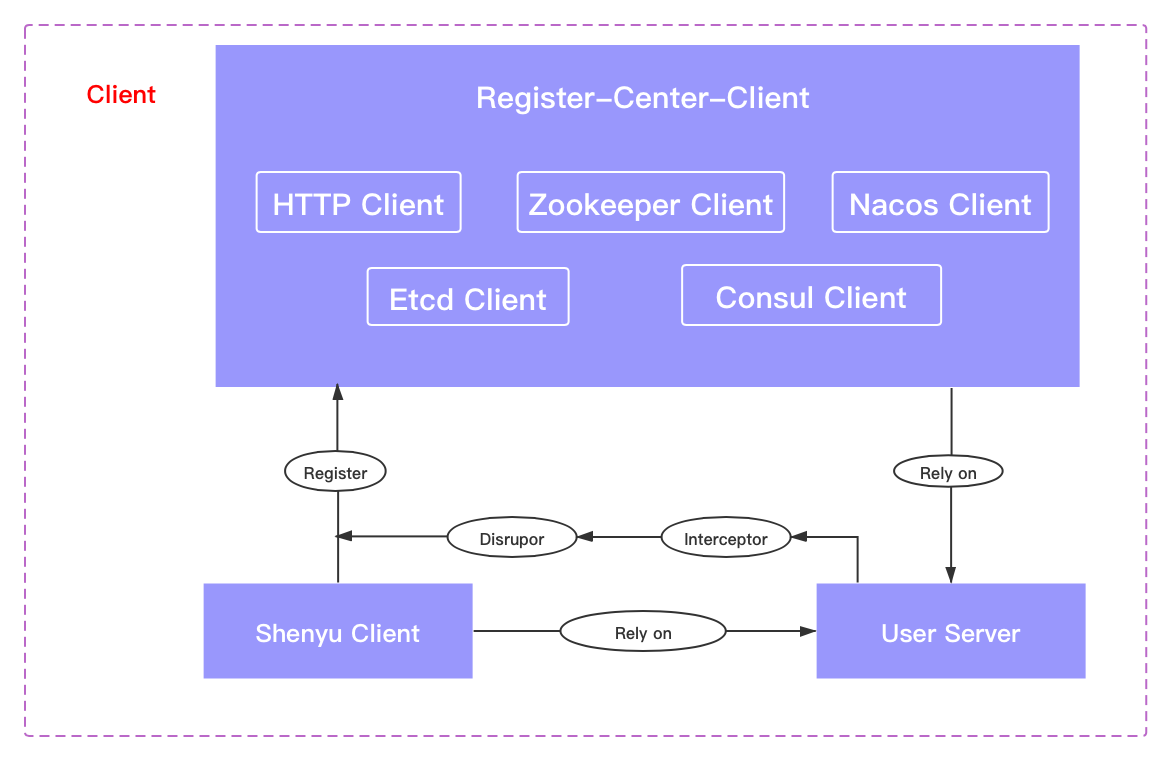
Declare the registry client type, such as Http or Zookeeper, in your microservice configuration.
Load and initialize the corresponding registry client using the SPI method when the application starts, and get the service interface information that needs to be registered in it by implementing the post-processor interface related to the Spring Bean, and put the obtained information into the Disruptor.
The registry client reads the data from Disruptor and registers the interface information to shenyu-admin, where Disruptor plays the role of decoupling data and operations, which is convenient for extension.
3.1.2 Server-side Registration
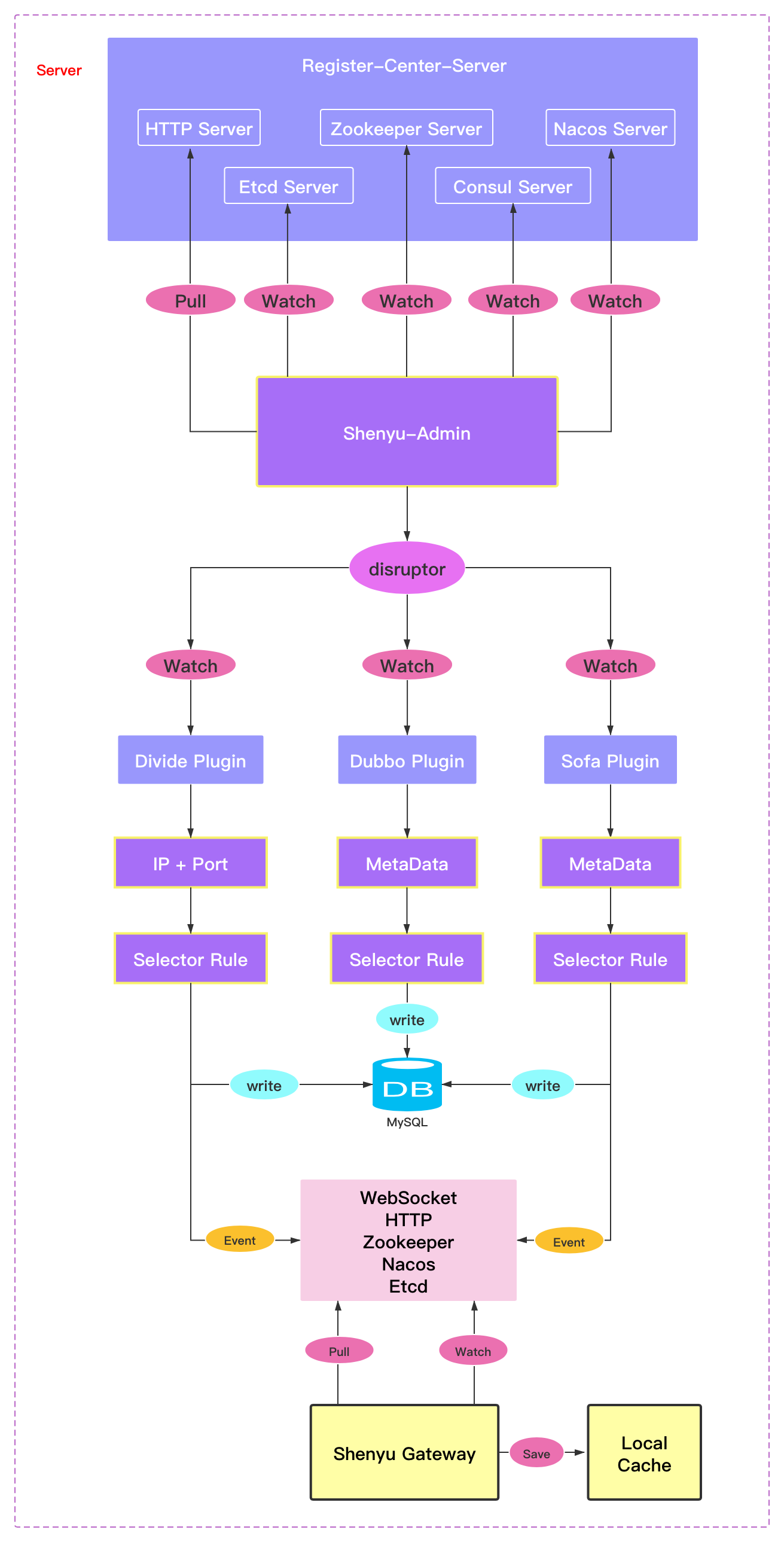
Declare the registry server type, such as Http or Zookeeper, in the shenyu-admin configuration. When shenyu-admin starts, it will read the configuration type, load and initialize the corresponding registry server, and when the registry server receives the interface information registered by shenyu-client, it will put it into Disruptor, and then it will trigger the registration processing logic to update the service interface information and publish the synchronization event.
The Disruptor plays a role in decoupling data and operation, which is good for extension. It also has a data buffering role if too many registration requests lead to registration exceptions.
3.2 Data Synchronization Principle
Data synchronization refers to the policy used to synchronize data to the Apache ShenYu gateway after the shenyu-admin backend has manipulated the data. The Apache ShenYu gateway currently supports ZooKeeper, WebSocket, Http long polling, Nacos, Etcd and Consul for data synchronization. The default is to synchronize data via WebSocket.
Please refer to [Data Synchronization Configuration](https://shenyu.apache.org/docs/user-guide/use-data-sync) for the configuration of data synchronization.
3.2.1 The Significance of Data Synchronization
The gateway is the entry point for traffic requests and plays a very important role in the microservices architecture, and the importance of high availability of the gateway is self-evident. In the process of using the gateway, in order to meet the business requirements, it is often necessary to change the configuration, such as flow control rules, routing rules and so on. Therefore, the dynamic configuration of the gateway is an important factor to ensure the high availability of the gateway.
The current data synchronization characteristics are as follows.
- All configurations are cached in the
Apache ShenYugateway memory, and each request uses the local cache, which is very fast. - Users can change any data in the
shenyu-adminbackend and it will be synchronized to the gateway memory immediately. - Supports data synchronization of plugins, selectors, rule data, metadata, signature data, etc. for
Apache ShenYu. - All plug-in selectors and rules are dynamically configured and take effect immediately, without restarting the service.
- Data synchronization method supports
Zookeeper,Http long polling,Websocket,Nacos,EtcdandConsul.
3.2.2 Data Synchronization Principle Analysis
The following diagram shows the flow of Apache ShenYu data synchronization. The Apache ShenYu gateway synchronizes configuration data from the configuration service when it starts, and supports push-pull mode to get configuration change information and then update the local cache. Administrators can change user permissions, rules, plugins, traffic configuration in the administration backend (shenyu-admin) and synchronize the changes to the Apache ShenYu gateway via push-pull mode, depending on which synchronization method is used.
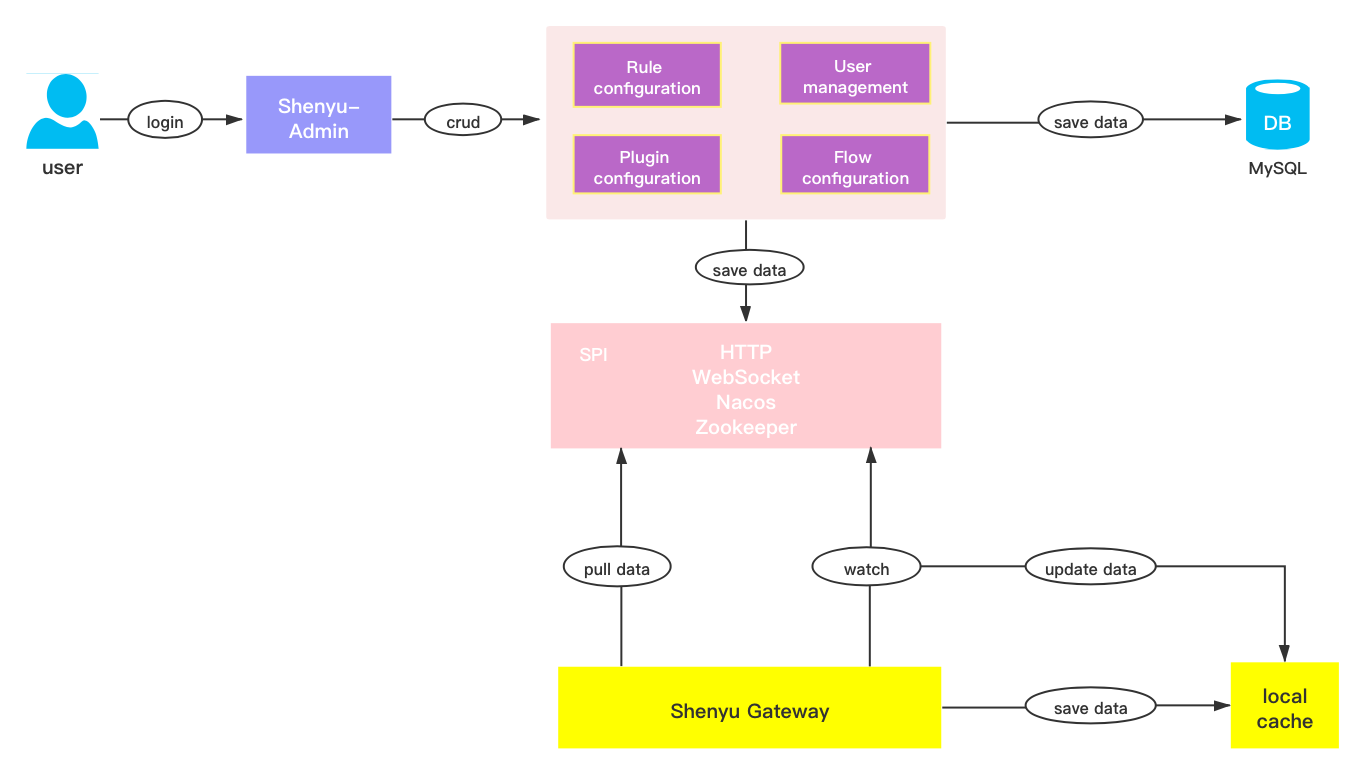
In the original version, the configuration service relied on the Zookeeper implementation, and the management backend pushed the changes to the gateway. Now we can support WebSocket, Http long polling, Zookeeper, Nacos, Etcd and Consul, by setting shenyu.sync.${strategy} in the configuration file to specify the corresponding synchronization strategy, the default is to use webosocket synchronization strategy to achieve second-level data synchronization. However, one thing to note is that the Apache ShenYu gateway and shenyu-admin must use the same synchronization strategy.
As shown in the figure below, shenyu-admin sends out configuration change notifications through EventPublisher after a user makes a configuration change, and EventDispatcher processes the change notification, and then synchronizes the data according to the configured synchronization policy (http, weboscket, zookeeper, naocs, etcd, consul). etcd, consul`), the configuration is sent to the corresponding event handler.
- If it is a
websocketsynchronization policy, the changed data will be actively pushed toshenyu-weband there will be a correspondingWebsocketDataHandlerprocessor at the gateway layer to handle the data push fromshenyu-admin. - In case of
zookeepersynchronization policy, the change data will be updated tozookeeper, andZookeeperSyncCachewill listen tozookeeperdata changes and process them. - In case of
httpsynchronization policy, the gateway initiates a long polling request with90stimeout by default, ifshenyu-adminhas no data change, it will block thehttprequest, if there is data change, it will respond with the changed data information, if more than60sthere is still no data change, it will respond with empty data, after the gateway layer receives the response After receiving the response, the gateway layer continues to makehttprequests, repeating the same requests.
3.3 Process Analysis
The process analysis shows the service registration process, data synchronization process and service invocation process from the source code perspective.
3.3.1 Service Registration Process
- Reading dubbo services
Use the annotation @ShenyuDubboClient to mark dubbo services that need to be registered to the gateway.
Annotation scanning is done via the ApacheDubboServiceBeanListener, which implements the ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> interface and starts executing the event handler method when a context refresh event occurs during the Spring container startup onApplicationEvent(). In the rewritten method logic, the Dubbo service ServiceBean is read, the metadata object and the URI object are constructed and registered with shenyu-admin.
The specific registration logic is implemented by the registry, please refer to [Client Access Principles](https://shenyu.apache.org/docs/design/register-center-design/) .
- Processing registration information
The metadata and URI data registered by the client through the registration center are processed at the shenyu-admin end, which is responsible for storing to the database and synchronizing to the shenyu gateway. The client-side registration processing logic of the Dubbo plugin is in the ShenyuClientRegisterDubboServiceImpl. The inheritance relationship is as follows.
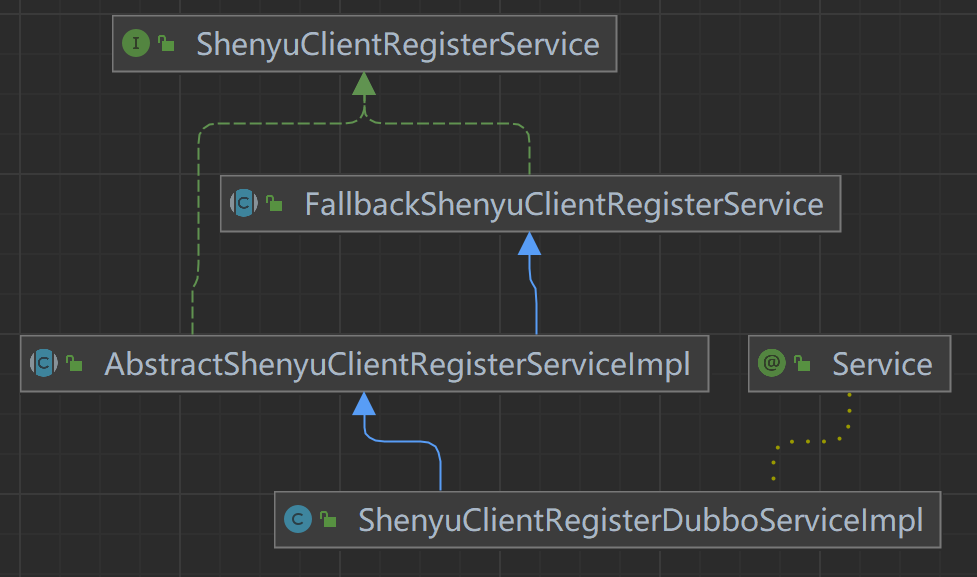
- ShenyuClientRegisterService: client registration service, top-level interface.
- FallbackShenyuClientRegisterService: registration failure, provides retry operation.
- AbstractShenyuClientRegisterServiceImpl: abstract class, implements part of the public registration logic.
- ShenyuClientRegisterDubboServiceImpl: implements the registration of
Dubboplug-ins.
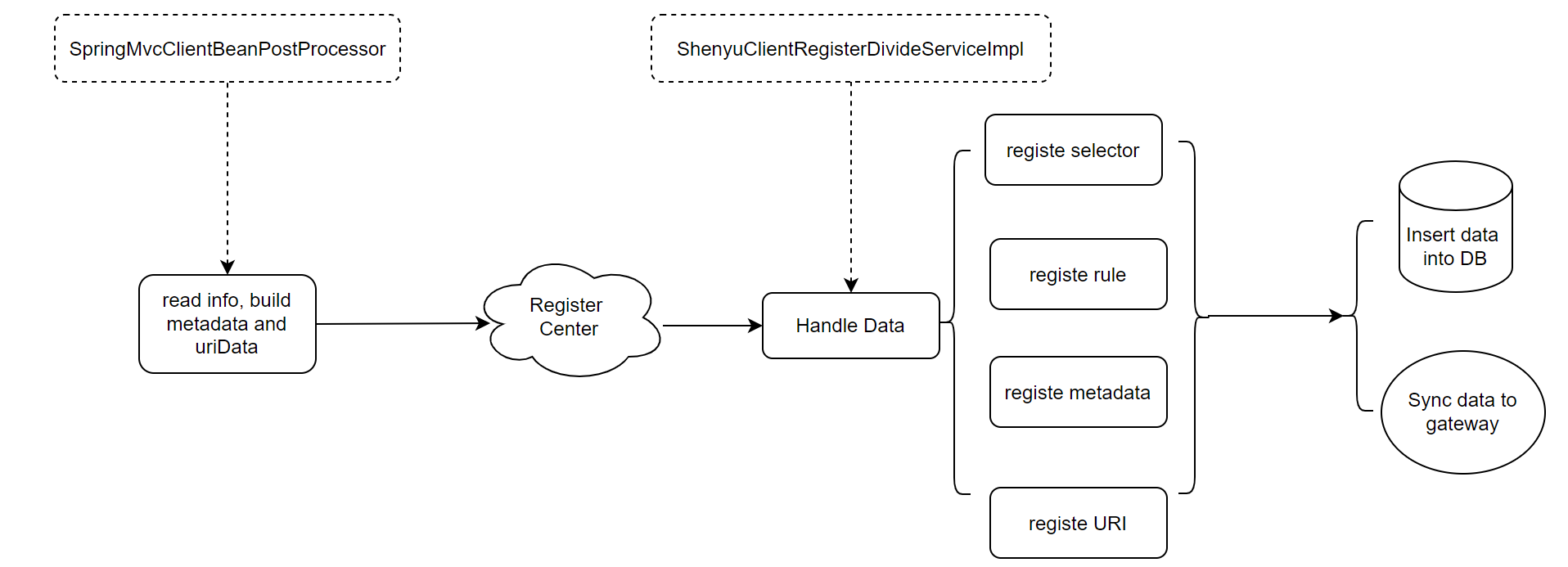
Registration information including selectors, rules and metadata.
The overall dubbo service registration process is as follows.
3.3.2 Data Synchronization Process
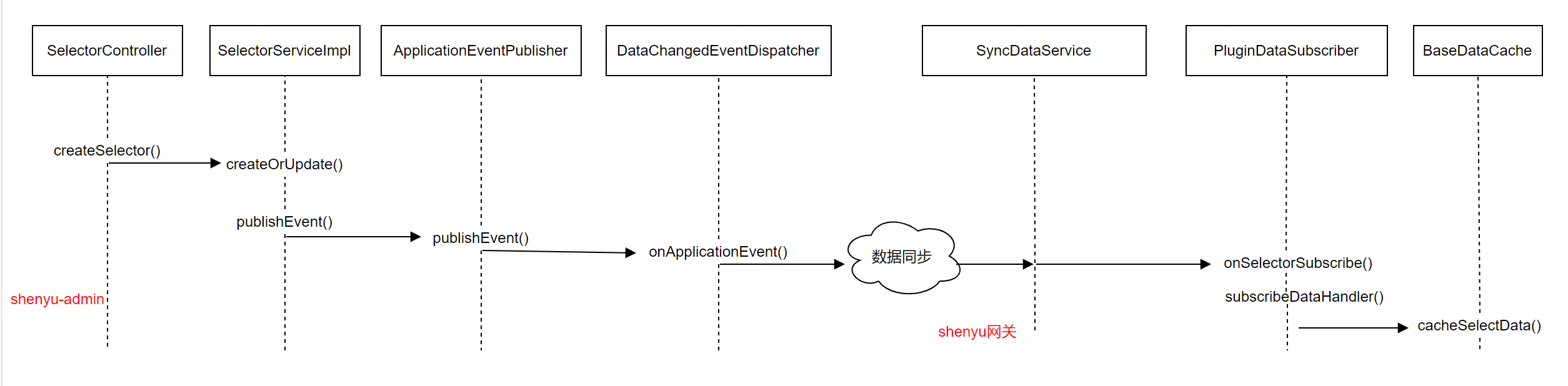
- admin update data
Suppose in the backend management system, a new selector data is added, the request goes to the createSelector() method in the SelectorController class, which is responsible for verifying the data, adding or updating the data, and returning the result information.
In the SelectorServiceImpl class, the createOrUpdate() method completes the conversion of the data, saves it to the database, publishes events, and updates the upstream.
Persistence of data is done in the Service class, i.e. saving data to the database. Publishing the changed data is done by eventPublisher.publishEvent(), the eventPublisher object is an ApplicationEventPublisher class, the fully qualified name of this class is org.springframework. ApplicationEventPublisher, the function of publishing data is exactly what is done through Spring related functions.
When the event is published, it automatically goes to the onApplicationEvent() method in the DataChangedEventDispatcher class, which handles the event according to the different data types and data synchronization methods.
- Gateway data synchronization
At startup, the gateway loads different configuration classes and initializes data synchronization-related classes according to the specified data synchronization method.
After receiving the data, it performs deserialization operation to read the data type and operation type. Different data types have different data processing methods, so there are different implementation classes. But they also have the same processing logic between them, so they can be implemented by template method design pattern. The same logic is put in the handle() method in the abstract class AbstractDataHandler, and the different logic is given to the respective implementation classes.
Adding a new selector data is a new operation that goes to the SelectorDataHandler.doUpdate() concrete data processing logic.
In the common plugin data subscriber CommonPluginDataSubscriber, which is responsible for handling all plugin, selector and rule information
Saves data to the gateway’s memory, BaseDataCache is the class that ultimately caches the data, implemented through the singleton pattern. The selector data is then stored in SELECTOR_MAP, a Map. In the subsequent use, the data is also taken from here.
The above logic is represented in a flowchart as follows.
3.3.3 Service Invocation Process
In the Dubbo plugin system, the class extends relationship is as follows.
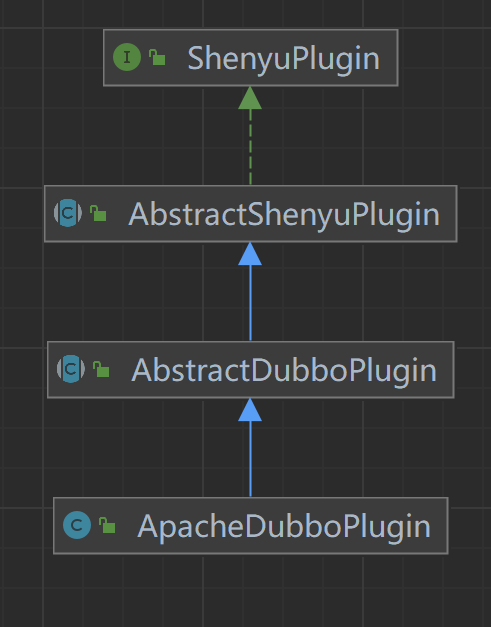
ShenyuPlugin: top-level interface, defining interface methods.
AbstractShenyuPlugin: abstract class that implements the common logic of the plugin; > AbstractShenyuPlugin: abstract class that implements the common logic of the plugin.
AbstractDubboPlugin: dubbo plug-in abstract class, implementing
dubbocommon logic (ShenYu gateway supports ApacheDubbo and AlibabaDubbo).ApacheDubboPlugin: ApacheDubbo plugin.
- org.apache.shenyu.web.handler.ShenyuWebHandler.DefaultShenyuPluginChain#execute()
After passing the ShenYu gateway proxy, the request entry is ShenyuWebHandler, which implements the org.springframework.web.server.WebHandler interface and connects all plugins through the chain-of-responsibility design pattern.
- org.apache.shenyu.plugin.base.AbstractShenyuPlugin#execute()
Determining whether a plugin is executed when a request is made to the gateway is done by the specified matching logic. The matching logic for selectors and rules is executed in the execute() method.
- org.apache.shenyu.plugin.global.GlobalPlugin#execute()
The first to be executed is the GlobalPlugin , which is a global plugin that constructs contextual information in the execute() method.
- org.apache.shenyu.plugin.base.RpcParamTransformPlugin#execute()
Next to be executed is the RpcParamTransformPlugin, which is responsible for reading the parameters from the http request, saving them in the exchange and passing them to the rpc service. In the execute() method, the core logic of the plugin is executed: it gets the request information from exchange and processes the parameters according to the form of the content passed in the request.
- org.apache.shenyu.plugin.dubbo.common.AbstractDubboPlugin
Then what gets executed is the DubboPlugin . In the doExecute() method, the main focus is on checking metadata and parameters. In the doDubboInvoker() method, special context information is set and then the generalized invocation of dubbo is started.
In the genericInvoker() method.
- Gets the
ReferenceConfigobject. - obtains the generalization service
GenericServiceobject. - Constructs the request parameter
pairobject. - Initiate an asynchronous generalization invocation.
The generalization call enables you to call the dubbo service at the gateway.
The ReferenceConfig object is the key object that supports generalization calls, and its initialization is done during data synchronization.
- org.apache.shenyu.plugin.response.ResponsePlugin#execute()
The last one to be executed is ResponsePlugin, which unifies the response result messages of the gateway. The processing type is determined by the MessageWriter, and the class extends relationship is as follows.
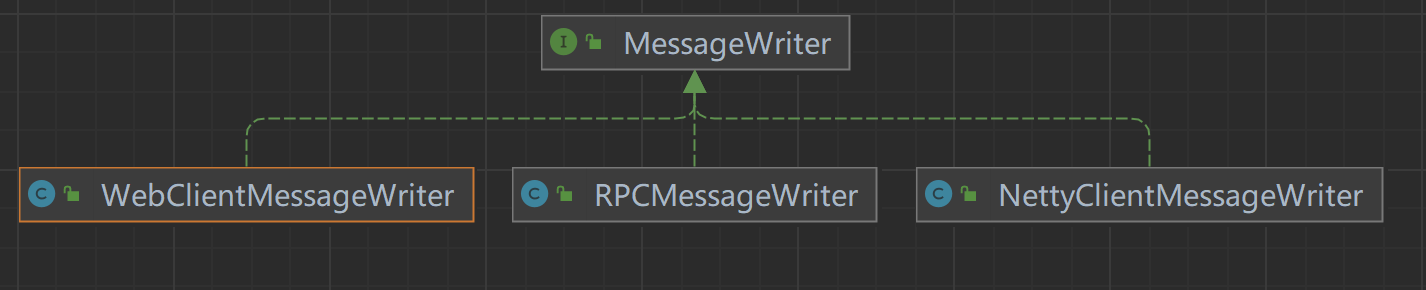
MessageWriter: interface that defines message processing methods.
NettyClientMessageWriter: Handles the results of
Nettycalls.RPCMessageWriter: processing the results of
RPCcalls.WebClientMessageWriter: processing the results of
WebClientcalls;
The Dubbo service is called and the result of processing is the RPCMessageWriter.
- org.apache.shenyu.plugin.response.strategy.RPCMessageWriter#writeWith()
Process the response results in the writeWith() method, get the results or handle exceptions.
At this point in the analysis, the source code analysis of the Dubbo plugin is complete, and the analysis flowchart is as follows.
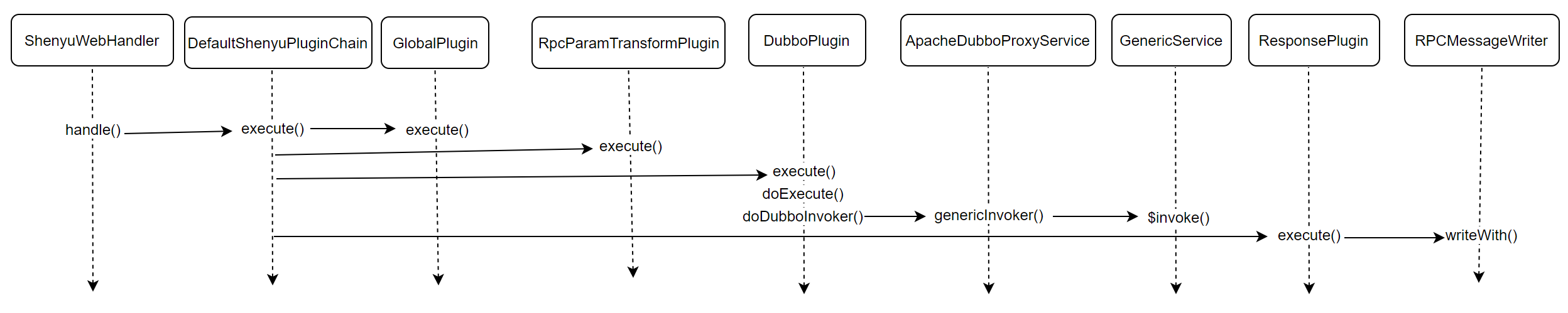
4. Summary
This article analyzes the proxy process of ShenYu gateway to Dubbo service from a practical case. The main knowledge points involved are as follows.
- Implementing plug-ins through the chain-of-responsibility design pattern.
- implementing
AbstractShenyuPluginusing the template method design pattern to handle generic operation types. - implementation of the cached data class
BaseDataCacheusing the singleton design pattern. - the ability to introduce different registries and number synchronization methods through the
springboot starter, which is very scalable. - support for hot updates of rules through
adminto facilitate traffic control. Disruptorqueue is for data and operation decoupling, as well as data buffering.