This article is more than one year old. Older articles may contain outdated content. Check that the information in the page has not become incorrect since its publication.
Can Apache Dubbo, Now a Decade Old, Ride the Waves Again?

Throughout the history of open source in China, it is hard to find a second project as controversial and discussed as Dubbo.
On one hand, its open source in 2011 filled the gap of RPC frameworks used in production environments, and it was widely adopted upon release; on the other hand, it experienced a halt in maintenance, a restart, donation to the Apache Foundation, and then graduated as a top-level project.
Facing skeptical developers, how will Apache Dubbo continue to shine in the cloud-native era?
This year marks the first anniversary of Dubbo’s graduation from the Apache Foundation and is also an important year for promoting Dubbo 3.0, which fully embraces cloud-native. Open Source China and Apache Dubbo have jointly planned the 【Dubbo Cloud Native Journey】 series of articles to review the development of the Apache Dubbo community. The series will primarily cover three main parts: technical interpretations of Dubbo, community updates, and application case analyses, and it will connect with everyone weekly.
Leave a message on the【Alibaba Cloud Native WeChat account】to share your story with Apache Dubbo, and the top ten liked participants can receive a special Dubbo prize cup; additionally, Apache Dubbo PMC member @Chickenlj will randomly draw a lucky reader to receive an eye protection lamp worth 260 yuan. The draw will take place next Wednesday.
Author Profile
Liu Jun, alias Lu Gui, GitHub account Chickenlj, Apache Dubbo PMC, core project developer, witnessed the entire process from Dubbo’s restart in open source to its graduation from the Apache Foundation. He is currently with Alibaba Cloud’s cloud-native application platform team, involved in service framework and microservices work, primarily promoting Dubbo 3.0 - Dubbo Cloud Native.
Series Opening: 3.0 Launched, One Year Since ASF Graduation
From 2019 until now, in the year since Dubbo’s graduation, both the Dubbo community and product have made significant progress, while the development of the cloud-native version - Dubbo 3.0 has also fully kicked off.
In the community aspect, two key points need to be highlighted: one is the increase in enterprise users participating and contributing, with over 200 mid-to-large companies proactively contacting the community, such as Ctrip, Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, Guazi Used Cars, UnionPay Clearing, Zhongtong, etc.; the other is the thriving sub-community represented by Dubbo-go.
In terms of product tech evolution, the Dubbo Java version has released 10 versions, deeply exploring multi-language, protocol, performance, and service governance models. Dubbo go has released over 8 versions, aligning its functionality with that of the Java version, and in some areas, it has taken the lead.
It is noteworthy that Alibaba is actively promoting the internal adaptation of the Dubbo community version, gradually realizing the upgrade of HSF framework internally using Dubbo from this year. This not only allows Alibaba to bring back its rich service governance experience from HSF to the community but also accelerates the development of Dubbo cloud-native directly.
In the wave of cloud-native, 3.0 has officially been set as the core goal for Dubbo’s product development this year, covering the next generation RPC protocol, service governance models, cloud-native infrastructure adaptation, and more. Many aspects have already been explored in the current 2.7 version, such as the recent release of HTTP/2 protocol support and application-level service discovery, establishing a foundation for future work. The series will also provide detailed analyses of the Dubbo 3.0 Roadmap and technical solutions.
One Year Since Dubbo Graduation Review
In July 2017, the Dubbo open-source project was reactivated, and in 2018 it was donated to the Apache Foundation. In May 2019, Dubbo graduated from incubation at the Apache Foundation and became an Apache top-level project. The following sections will introduce Dubbo’s achievements over the past year in terms of community, sub-communities, and products.
Community Released 24 Versions in a Year, Contributors Exceed 300
If the early reactivation was primarily led by Alibaba’s project maintenance investment, Dubbo has become a fully open foundation project led by the community and primarily contributed to by the community since joining Apache.
Today, this trend is becoming more evident. Internet and traditional companies, including Alibaba, Ctrip, Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, Guazi Used Cars, UnionPay Clearing, and Zhongtong, have made contributions in using Dubbo and community code contributions. The Dubbo community is becoming very active and diverse.
In the past year, the Dubbo community project has released a total of 24 versions and developed 27 Committer/PMC members, of which 20% of contributors are from Alibaba, while over 80% come from various organizations of developers or enthusiasts.
The Dubbo community organized more than 10 offline meetup events, basically covering cities where developers gather domestically. Through offline or online live events, more than 100 topics were shared, deeply explaining Dubbo community’s latest dynamics, functional module development, and recent plans. Most keynote speeches are gathered from deep enterprises sharing practical experience, with typical representatives including Ctrip, Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, Koala, and Credit Computing Power.
From GitHub statistics, Dubbo Star has achieved a new milestone, surpassing 30,000, which is nearly five times higher than when it was restarted; contributors have grown from tens to over 300, with more than 60 nominated as committers. Both the number of contributors and the ratio of committers have significantly increased; there have been 65 releases of Dubbo Java.
The above primarily summarizes the community development of the Dubbo Java project; the following will introduce the advancements in Dubbo Java products.
Dubbo Java Iteration, Currently Mainly Maintaining 3 Major Versions
The main major versions maintained by the community currently are 2.5.x, 2.6.x, and 2.7.x.
- 2.7.x is the community’s primary development version, releasing 8 versions in the past year (2.7.0 - 2.7.7), each featuring noteworthy enhancements or upgrades across multiple aspects from programming models, service governance, performance to protocols;
- The 2.6.x version is designated as a bugfix version, with 3 versions released in the past year, mainly fixing issues and security vulnerabilities without adding many new features;
- The 2.5.x version was declared EOF at the beginning of 2019 and has only undergone security fixes; by the second half of the year, maintenance had completely stopped.
Below is a brief layered module diagram recounting the evolution of Dubbo’s technical architecture from aspects like programming model, service governance, transmission protocol, and performance optimization:
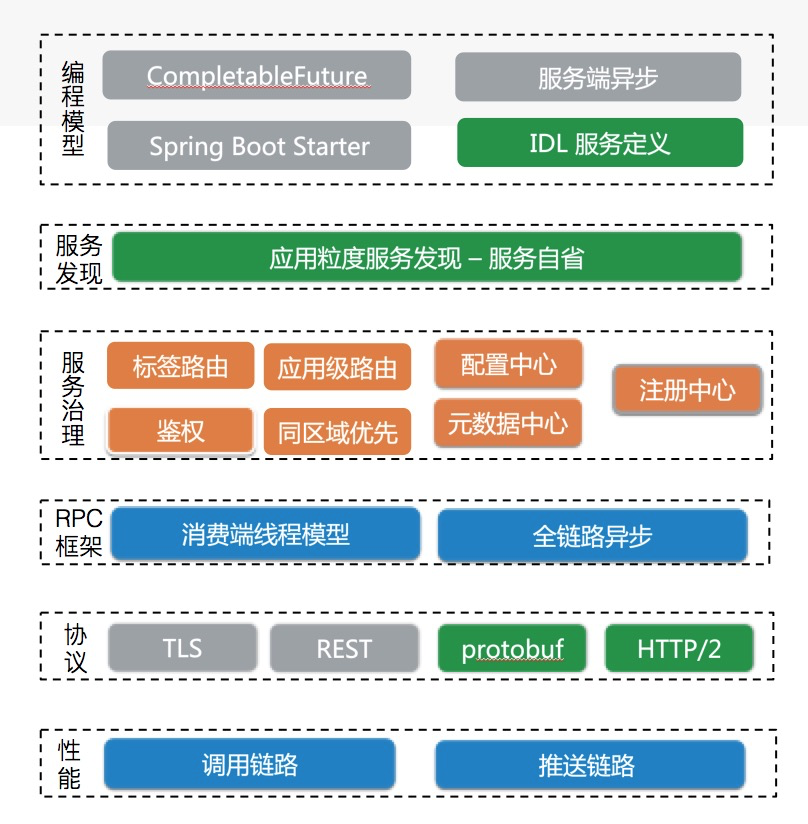
Many of the above functions have been implemented by major vendors to solve specific business problems. We also look forward to more in-depth summaries of Dubbo practices brought by these vendors in the future.
Dubbo-go’s Fifth Year Developments in Parallel with Dubbo
Apart from Dubbo Java, many excellent sub-projects (sub-communities) have also been developed around Dubbo, including Dubbo-spring-boot-project, Dubbo-go, etc. Here, we will focus on introducing the Dubbo-go sub-community.
The Dubbo-go project was first built in May 2016 and released and open-sourced in September of the same year. The timeline below clearly records Dubbo-go’s origins and developments.

Inheriting the natural mission of “bridging the gap between Java and Go”, Dubbo-go has now entered its fifth year and has carved out its unique development path:
- The current v1.4.0 version aligns with the 2.6.x version, with the upcoming version set to align with v2.7.x【matching v2.7.5】, and thereafter release the v1.6.0 version corresponding to Dubbo 3.x;
- Independently maintain the complete implementation of the underlying hessian2 protocol library Dubbo-go-hessian2, network library getty, to the upper layer aligning with Dubbo;
- Independent TCP + Protobuf and gRPC + JSON communication solutions have been developed【to be included in version v1.5.0】;
- Already achieved interoperability with Dubbo/gRPC/Spring Boot;
- By integrating Opentracing and Prometheus, Dubbo-go has embarked on its unique explorations in observability and other microservice directions;
- Achieved trusted RPC calling based on HTTPS[https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzU4NzU0MDIzOQ==&mid=2247489539&idx=3&sn=379514cac71b91d57643e6f3d2701cdf&scene=21#wechat_redirect];
- Developed its unique microservice solutions using Kubernetes as a registry[https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzU4NzU0MDIzOQ==&mid=2247489465&idx=3&sn=514144ef1a217a50b9f5a640ca122ac8&scene=21#wechat_redirect];
Dubbo-go has evolved from its initial implementation of Dubbo in Go language to currently being the most powerful among Dubbo’s multi-language versions, with its development backed by the strong Dubbo-go community. In addition to the above characteristics, cross-community collaboration has achieved the following results:
- Through collaboration with the MOSN community, Dubbo/Dubbo-go applications can seamlessly integrate with the Dubbo Mesh based on MOSN, realizing coexistence of microservices and cloud-native in a “dual-mode microservices”;
- Collaborated with the Sentinel community to seamlessly integrate downgrade and rate limiting solutions into Dubbo/Dubbo-go;
- Partnered with the Apollo community to implement remote configuration rollout in Dubbo-go;
- Collaborated with the Nacos community for service discovery based on Nacos;
The Dubbo-go community’s primary goals for Q2 2020 include:
- Release v1.5.0 fully aligning with Dubbo 2.7.x;
- Release v1.6.0 that matches Dubbo 3.0;
- Continue exploration in cloud-native aspects;
- Maintain cooperative momentum with brother communities to expand usability;
- Advance production practices within Alibaba Group and other vendors.
The project (including sub-projects) has been successfully implemented in companies such as Ctrip, Tuya Smart, and Ant Group.
This year, after the integration of HSF and Dubbo within Alibaba Group, the project will also be tested in the Alibaba Group’s Double Eleven battlefield.
Cloud-Native Dubbo - Dubbo 3.0
3.0 is the codename for the next-generation Dubbo architecture. A year ago, during the initial exploration of Reactive Streams, the community had extensive discussions about Dubbo 3.0. Now, against the backdrop of cloud-native, 3.0 represents a more comprehensive upgrade of the Dubbo architecture, covering the next generation RPC protocol, a brand-new service governance model, and adaptation to cloud-native infrastructure.
Alibaba is one of the main forces involved in the development and construction of Dubbo 3.0. This Alibaba-originated open-source project is returning to internal implementation at Alibaba.
Since last year, Alibaba has been gradually promoting the replacement of its internal HSF framework with Dubbo, integrating the two frameworks and developing a Dubbo version suited for cloud-native architecture based on this integration. The return of Dubbo to Alibaba’s implementation represents a great practice of embracing the community, cloud-native, and standardization.
The internal rollout of Dubbo 3.0 at Alibaba is a significant benefit for the community, enabling Alibaba to share its rich service governance experience from HSF back to the community and directly driving the rapid evolution of Dubbo’s cloud-native architecture. Aside from Alibaba, vendors like Douyu, Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, and iQIYI are also involved in the construction of the next-generation Dubbo 3.0.
The following lists three important directions in Dubbo 3.0; the specific Roadmap will be explained separately in upcoming articles:
- Next-generation RPC protocol. The new protocol will provide richer built-in semantics such as Stream, Flow Control, and will have better extensibility and friendlier gateway compatibility;
- Application-granularity-based service discovery mechanism. Balancing Dubbo’s interface-oriented usability and functionality, the aim is to resolve compatibility issues with Kubernetes Native Services and address performance bottlenecks in address pushing within large clusters;
- Solutions to adapt to cloud-native infrastructures. This involves aligning Dbubo service and infrastructure lifecycle, adapting to Kubernetes Native Service, services governance rules compliant with infrastructure scheduling, solutions for integrating Service Mesh architecture, etc.;
Let’s briefly expand on these three aspects.
Next-Generation RPC Protocol
Focusing on the protocol itself, the next-generation protocol mainly centers around HTTP/2, Reactive Streams, Flow Control, etc.:
- Reactive Stream: Introduces RPC, providing richer communication semantics and support for API programming models such as Request-Stream, Bi-Stream, etc.;
- HTTP/2: Communication protocols built on HTTP/2 for microservices in cloud-native scenarios have better universality and penetration;
- Flow Control: Built-in flow control mechanisms support request (n) flow control mechanisms similar to Reactive Streams.
From the perspective of solving business scenario problems, based on the new protocol, Dubbo at the framework level will support intelligent decision-making load balancing algorithms, become friendlier to Mesh and gateways, and provide easier multi-language implementations and interoperability.
- Mesh: The protocol is more friendly in penetrating Mesh, distinguishing protocol headers Metadata from RPC Payload, facilitating cooperation with Mesh, including flow control mechanisms and application-level configuration negotiations;
- Protocol Universality: Balancing universality and performance, ensuring protocols can run on various devices;
- Multi-Language Support: For instance, by supporting Protobuf, more comprehensive cross-language service definitions and serialization support are provided.
Application-Level Service Governance
Being interface-oriented has always been a strength of the Dubbo framework. Its ease of use shields developers from the complexity of remote calls; at the same time, the interface-oriented address discovery and service governance provide more robust capabilities, making the entire Dubbo governance system very strong and flexible.
Given the many benefits of being interface-oriented, why should we also explore application-oriented governance models?
It may sound contradictory. In fact, whether interface-oriented or application-oriented is just a different perspective on looking at Dubbo. What we refer to as “interface-oriented -> application-oriented” transformation mainly reflects the changes in service registration and discovery:
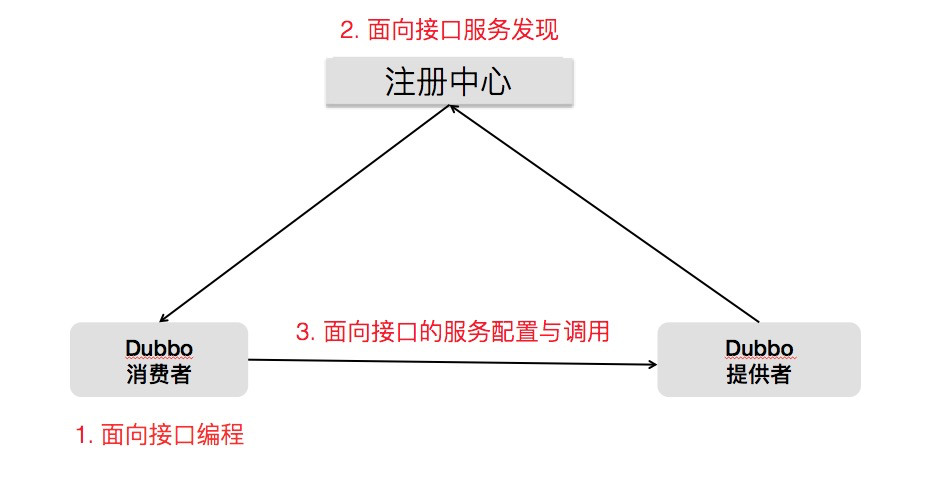
The new application-oriented model focuses on the second point, which transforms the data organization in the registry center to an “application/instance” granularity. This addresses two problems:
- Aligning with microservice models such as Kubernetes Services at service discovery levels;
- Reducing the amount of data in service discovery from “number of interfaces * number of instances” to “number of applications * number of instances”.
For more details, refer to the article “Dubbo Takes an Important Step Towards Cloud Native - Analysis of Application-Level Service Discovery”, and this series will also include deeper analyses of this mechanism and its implementation.
Cloud-Native Infrastructure
Cloud-native brings encompassing changes to the underlying infrastructure, application development, deployment, and operations:
Infrastructure
- Changes in infrastructure scheduling mechanisms, leading to changes in operations (lifecycle), service governance, etc.;
- Service discovery capabilities are being decentralized, with Kubernetes abstracting Native Service Discovery.
Service Mesh - Cloud-Native Microservices Solutions
- Mesh provides solutions for cross-language and SDK upgrades; the Dubbo SDK needs to collaborate with Mesh to achieve functional, protocol, service governance, and other adaptations;
- Mesh has not been widely rolled out yet; its suitability is more geared towards applications that focus on traffic control, and the performance advantages of traditional SDKs still exist; mixed deployment scenarios might persist for a long time.
Application scenarios for Dubbo’s deployment may include:
- Not using Kubernetes Native Service, where Kubernetes serves solely as a container orchestration and scheduling facility, continuing to use the self-built service registration and discovery mechanisms in Dubbo;
- Reutilizing Kubernetes Native Service, where Dubbo no longer concerns itself with service registration and Dubbo Client is responsible for service discovery and traffic allocation;
- Transitioning Dubbo SDK towards Mesh, where it needs to adapt to Mesh architecture, establishing an RPC programming and communication solution under the Mesh system; used to ensure long-term coexistence and interoperability of service discovery and governance systems between Dubbo and Mesh architectures;
- Smooth migration support for hybrid deployments between K8S and non-cloud environments, including unification of service discovery and facilitation of network communication solutions.
From Dubbo’s functional perspective, support for cloud-native infrastructures will focus on the following areas:
- Lifecycle: Binding Dubbo with Kubernetes scheduling mechanisms to keep service lifecycles autonomously aligned with Pod container lifecycles;
- Governance Rules: Optimizing service governance rules in terms of rule bodies and formats, such as describing rule bodies in YAML, eliminating dependencies on filtering rules for IPs, and defining unique CRD resources for rules;
- Service Discovery: Supporting service discovery of K8S Native Service, including DNS and API-Server, supporting xDS for service discovery;
- Mesh Architecture Collaboration: Building next-generation communication protocols based on HTTP/2 and supporting standardized data dispatching for xDS.
The next-generation RPC protocol and application-level service discovery model will serve as foundational elements of this part.
Summary and Outlook
As the opening of the series of articles, we provided a brief summary and review of Dubbo’s achievements over the past year, including the development of the Dubbo community and product iterations. Next, we will see more in-depth experience sharing from deep Dubbo users and the development stories of the Dubbo-go sub-community. More importantly, we have also projected the next-generation cloud-native Dubbo - Dubbo 3.0, with future releases regarding the Dubbo 3.0 Roadmap, design plans, and progress analyses set to be published in this series.