This article is more than one year old. Older articles may contain outdated content. Check that the information in the page has not become incorrect since its publication.
Dubbo Integrates Nacos as a Registry Center
Nacos is an important registry center implementation in the Dubbo ecosystem, and dubbo-registry-nacos is the implementation for integrating Nacos as a registry center in Dubbo.
Preparations
Before integrating dubbo-registry-nacos into your Dubbo project, make sure that the Nacos service is started in the background. If you are not familiar with the basic usage of Nacos, you can refer to the Nacos Quick Start. It is recommended to use Nacos version 0.6.1 or above.
Quick Start
Integrating Nacos as a registry center in Dubbo is straightforward and can be summarized into two main steps: “add Maven dependencies” and “configure the registry”.
Add Maven Dependencies
First, add the dubbo-registry-nacos Maven dependency to your project’s pom.xml file, and it is strongly recommended to use Dubbo 2.6.5:
<dependencies>
...
<!-- Dubbo Nacos registry dependency -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-registry-nacos</artifactId>
<version>0.0.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Keep latest Nacos client version -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.nacos</groupId>
<artifactId>nacos-client</artifactId>
<version>[0.6.1,)</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Dubbo dependency -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo</artifactId>
<version>2.6.5</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Alibaba Spring Context extension -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.spring</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId>
<version>1.0.2</version>
</dependency>
...
</dependencies>
After adding dubbo-registry-nacos to the project, you don’t need to explicitly program the service discovery and registration logic, as the actual implementation is provided by this third-party package. Next, configure the Nacos registry.
Configure the Registry
Assuming your Dubbo application uses the Spring Framework for configuration, there are two configuration methods available: Dubbo Spring Externalized Configuration and Spring XML configuration file. The author strongly recommends the former.
Dubbo Spring Externalized Configuration
Dubbo Spring externalized configuration is a new feature introduced in Dubbo 2.5.8, which automatically generates and binds Dubbo configuration beans through Spring Environment properties, simplifying configuration and lowering the threshold for microservice development.
Assuming your Dubbo application uses Zookeeper as the registry center, and its server IP address is: 10.20.153.10, while the registry address is stored as a Dubbo externalized configuration property in the dubbo-config.properties file, as shown below:
## application
dubbo.application.name = your-dubbo-application
## Zookeeper registry address
dubbo.registry.address = zookeeper://10.20.153.10:2181
...
Assuming your Nacos Server also runs on server 10.20.153.10 and uses the default Nacos server port 8848, you only need to adjust the dubbo.registry.address property as follows:
## Other properties remain unchanged
## Nacos registry address
dubbo.registry.address = nacos://10.20.153.10:8848
...
Then, restart your Dubbo application, and the Dubbo service provider and consumer information can be displayed in the Nacos console:
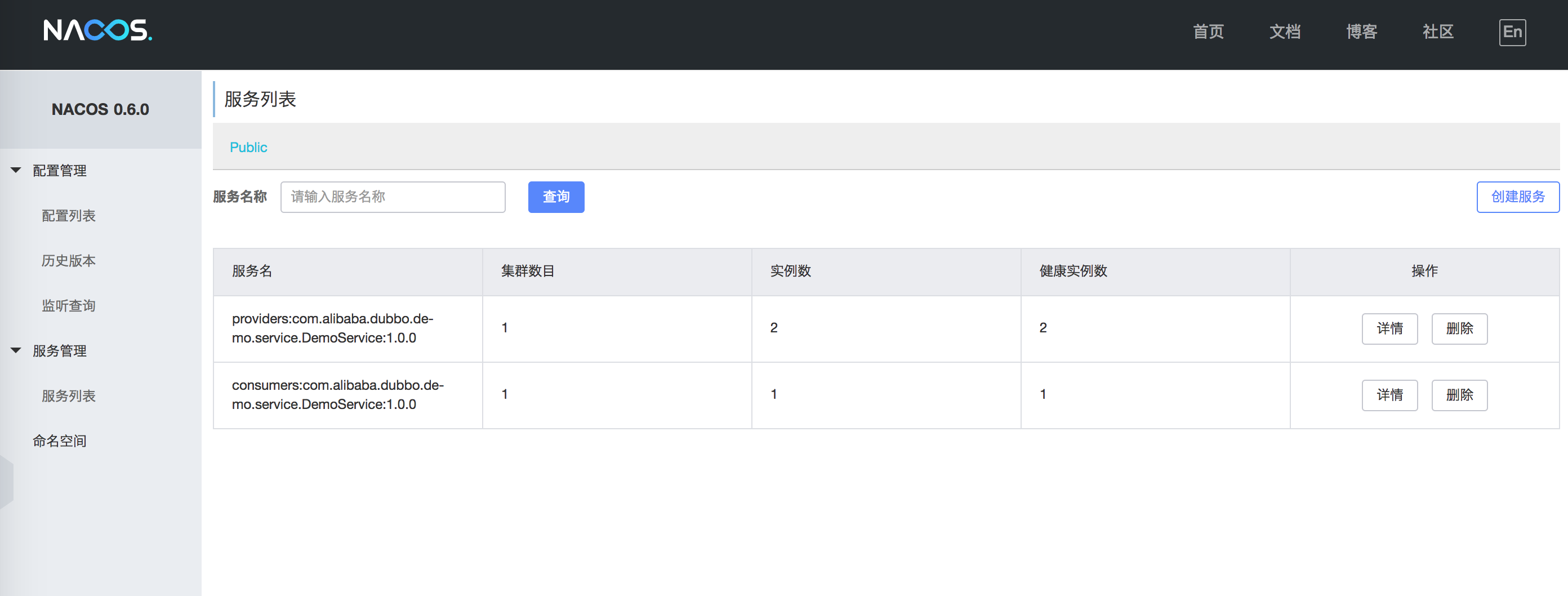
As shown in the figure, the information prefixed with providers: represents metadata of service providers, while consumers: represents metadata of service consumers. Click “Details” to see the service status details:
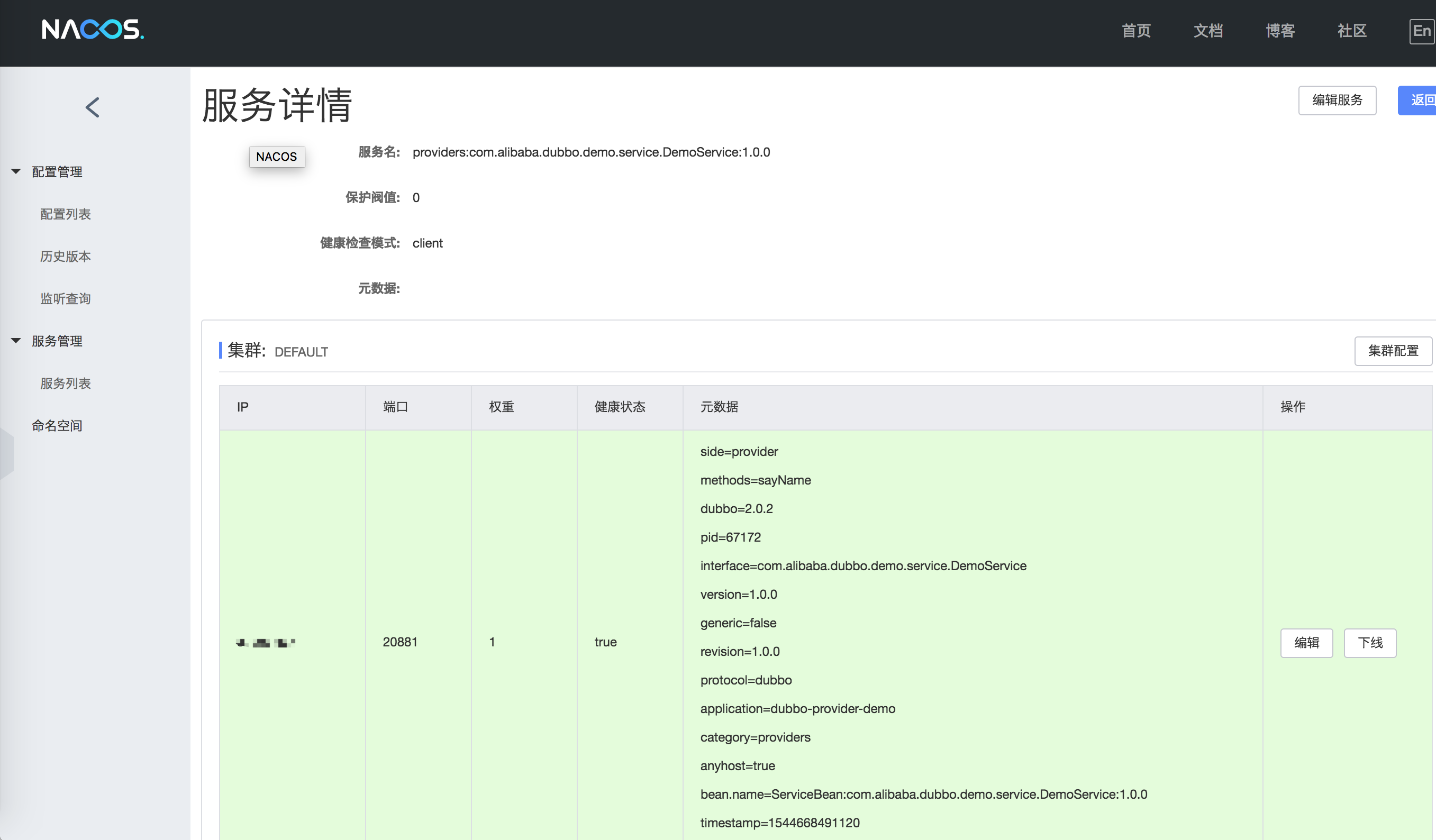
If you are using Spring XML configuration file to configure the Dubbo registry, please refer to the next section.
Spring XML Configuration File
Similarly, if your Dubbo application uses Zookeeper as the registry and its server IP address is: 10.20.153.10, and you configure Spring Beans in an XML file as shown below:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<!-- Provider application info for dependency calculation -->
<dubbo:application name="dubbo-provider-xml-demo" />
<!-- Use Zookeeper registry -->
<dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://10.20.153.10:2181" />
...
</beans>
Similar to Dubbo Spring Externalized Configuration, simply adjust the address property configuration:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<!-- Provider application info for dependency calculation -->
<dubbo:application name="dubbo-provider-xml-demo" />
<!-- Use Nacos registry -->
<dubbo:registry address="nacos://10.20.153.10:8848" />
...
</beans>
After restarting the Dubbo application, you can also find the registered metadata of service providers and consumers displayed in the Nacos console:
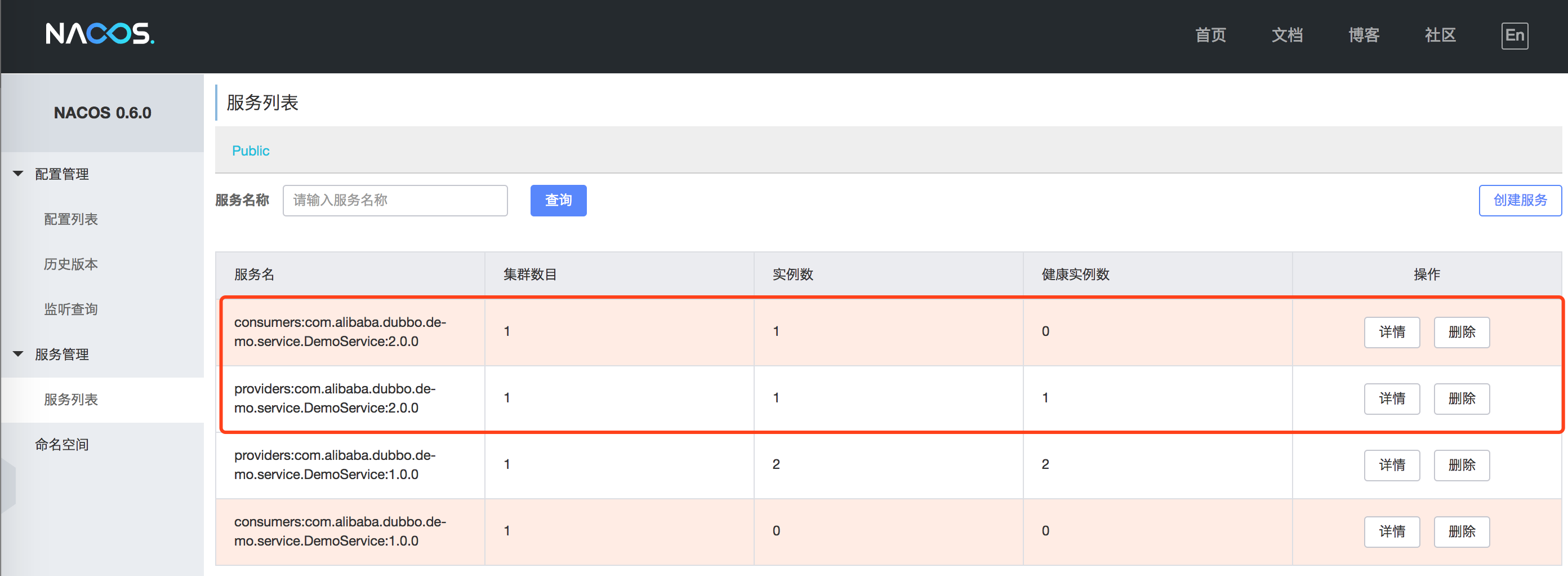
Is configuring or switching to Nacos registry super easy? If you are still unclear or want more details, you may refer to the complete example below.
Complete Example
The metadata in the images above comes from the Dubbo Spring annotation-driven example and the Dubbo Spring XML configuration-driven example. Below, we will introduce both, and you can choose your preferred programming model. Before discussing, let’s introduce the preparations for both, as they both rely on Java service interface and implementation. Meanwhile, please ensure that the local environment (127.0.0.1) has Nacos service running.
Example Interface and Implementation
First, define the example interface as follows:
package com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.service;
/**
* DemoService
*
* @since 2.6.5
*/
public interface DemoService {
String sayName(String name);
}
The implementation class providing the above interface:
package com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.service;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.config.annotation.Service;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcContext;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
/**
* Default {@link DemoService}
*
* @since 2.6.5
*/
@Service(version = "${demo.service.version}")
public class DefaultService implements DemoService {
@Value("${demo.service.name}")
private String serviceName;
public String sayName(String name) {
RpcContext rpcContext = RpcContext.getContext();
return String.format("Service [name :%s , port : %d] %s(\"%s\") : Hello,%s",
serviceName,
rpcContext.getLocalPort(),
rpcContext.getMethodName(),
name,
name);
}
}
With the interface and implementation ready, we will now implement both annotation-driven and XML configuration-driven versions.
Spring Annotation-Driven Example
Dubbo 2.5.7 refactored the programming model for Spring annotation-driven applications.
Service Provider Annotation-Driven Implementation
- Define the externalized configuration properties source for Dubbo provider -
provider-config.properties
## application
dubbo.application.name = dubbo-provider-demo
## Nacos registry address
dubbo.registry.address = nacos://127.0.0.1:8848
## Dubbo Protocol
dubbo.protocol.name = dubbo
dubbo.protocol.port = -1
# Provider @Service version
demo.service.version=1.0.0
demo.service.name = demoService
- Implement the service provider bootstrap class -
DemoServiceProviderBootstrap
package com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.provider;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.config.spring.context.annotation.EnableDubbo;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.service.DemoService;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* {@link DemoService} provider demo
*/
@EnableDubbo(scanBasePackages = "com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.service")
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:/provider-config.properties")
public class DemoServiceProviderBootstrap {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.register(DemoServiceProviderBootstrap.class);
context.refresh();
System.out.println("DemoService provider is starting...");
System.in.read();
}
}
The @EnableDubbo annotation activates Dubbo’s annotation-driven mode and externalized configuration, with the scanBasePackages attribute scanning the specified Java package to expose all service interface implementation classes marked with @Service as Spring Beans, which are subsequently exported as Dubbo services.
The @PropertySource annotation, introduced in Spring Framework 3.1, standardizes importing externalized configuration resources for Dubbo.
Service Consumer Annotation-Driven Implementation
- Define the externalized configuration properties source for Dubbo consumer -
consumer-config.properties
## Dubbo Application info
dubbo.application.name = dubbo-consumer-demo
## Nacos registry address
dubbo.registry.address = nacos://127.0.0.1:8848
# @Reference version
demo.service.version= 1.0.0
Similarly, the dubbo.registry.address property points to the Nacos registry, and other Dubbo service-related metadata is obtained through the Nacos registry.
- Implement the service consumer bootstrap class -
DemoServiceConsumerBootstrap
package com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.consumer;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.config.annotation.Reference;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.config.spring.context.annotation.EnableDubbo;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.service.DemoService;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* {@link DemoService} consumer demo
*/
@EnableDubbo
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:/consumer-config.properties")
public class DemoServiceConsumerBootstrap {
@Reference(version = "${demo.service.version}")
private DemoService demoService;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(demoService.sayName("Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)"));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.register(DemoServiceConsumerBootstrap.class);
context.refresh();
context.close();
}
}
Similarly, the @EnableDubbo annotation activates Dubbo’s annotation-driven mode and externalized configuration. However, as this is a service consumer, there is no need to specify the Java package name scanning for service implementations marked with @Service.
The @Reference annotation is used for dependency injection of Dubbo remote services, where the service provider and consumer agree on interface, version, and group information. In this service consumer example, the service version of DemoService is sourced from the property configuration file consumer-config.properties.
The @PostConstruct code indicates that when the DemoServiceConsumerBootstrap Bean is initialized, it executes ten remote method calls via Dubbo.
Run the Annotation-Driven Example
Start two instances of the DemoServiceProviderBootstrap locally, and you will see two healthy services appearing in the registry:

Then run the DemoServiceConsumerBootstrap, and the output will be as follows:
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)") : Hello,Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)
Service [name :demoService , port : 20881] sayName("Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)") : Hello,Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)") : Hello,Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)") : Hello,Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)
Service [name :demoService , port : 20881] sayName("Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)") : Hello,Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)
Service [name :demoService , port : 20881] sayName("Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)") : Hello,Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)") : Hello,Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)") : Hello,Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)
Service [name :demoService , port : 20881] sayName("Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)") : Hello,Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)
Service [name :demoService , port : 20881] sayName("Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)") : Hello,Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)
The execution is correct, and the service consumer uses a load balancing strategy, distributing the ten RPC calls evenly across the two Dubbo service provider instances.
Spring XML Configuration Driven Example
Spring XML configuration driven is the traditional programming model for assembling Spring components.
Service Provider XML Configuration Driven
- Define the service provider XML context configuration file -
/META-INF/spring/dubbo-provider-context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<!-- Provider application info for dependency calculation -->
<dubbo:application name="dubbo-provider-xml-demo"/>
<!-- Use Nacos registry -->
<dubbo:registry address="nacos://127.0.0.1:8848"/>
<!-- Expose services with dubbo protocol on random ports -->
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="-1"/>
<!-- Declare services that need to be exposed -->
<dubbo:service interface="com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.service.DemoService" ref="demoService" version="2.0.0"/>
<!-- Implement service like local bean -->
<bean id="demoService" class="com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.service.DefaultService"/>
</beans>
- Implement the service provider bootstrap class -
DemoServiceProviderXmlBootstrap
package com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.provider;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.service.DemoService;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* {@link DemoService} provider demo XML bootstrap
*/
public class DemoServiceProviderXmlBootstrap {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext();
context.setConfigLocation("/META-INF/spring/dubbo-provider-context.xml");
context.refresh();
System.out.println("DemoService provider (XML) is starting...");
System.in.read();
}
}
Service Consumer XML Configuration Driven
- Define the service consumer XML context configuration file -
/META-INF/spring/dubbo-consumer-context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<!-- Provider application info for dependency calculation -->
<dubbo:application name="dubbo-consumer-xml-demo"/>
<!-- Use Nacos registry -->
<dubbo:registry address="nacos://127.0.0.1:8848"/>
<!-- Reference service interface -->
<dubbo:reference id="demoService" interface="com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.service.DemoService" version="2.0.0"/>
</beans>
- Implement the service consumer bootstrap class -
DemoServiceConsumerXmlBootstrap
package com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.consumer;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.service.DemoService;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* {@link DemoService} consumer demo XML bootstrap
*/
public class DemoServiceConsumerXmlBootstrap {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext();
context.setConfigLocation("/META-INF/spring/dubbo-consumer-context.xml");
context.refresh();
System.out.println("DemoService consumer (XML) is starting...");
DemoService demoService = context.getBean("demoService", DemoService.class);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(demoService.sayName("Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)"));
}
context.close();
}
}
Run XML Configuration Driven Example
Again, start two instances of DemoServiceProviderXmlBootstrap, and observe changes in the Nacos registry for service providers:

The service version for the XML configuration-driven example is 2.0.0, and thus the service registration is correct.
Now run the service consumer bootstrap class DemoServiceConsumerXmlBootstrap and observe the console output:
Service [name :null , port : 20882] sayName("Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)") : Hello,Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)
Service [name :null , port : 20882] sayName("Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)") : Hello,Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz")
Service [name :null , port : 20883] sayName("Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)") : Hello,Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz")
Service [name :null , port : 20882] sayName("Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)") : Hello,Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz")
Service [name :null , port : 20882] sayName("Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)") : Hello,Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz")
Service [name :null , port : 20883] sayName("Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)") : Hello,Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz")
Service [name :null , port : 20882] sayName("Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)") : Hello,Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz")
Service [name :null , port : 20883] sayName("Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)") : Hello,Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz")
Service [name :null , port : 20883] sayName("Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)") : Hello,Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz")
Service [name :null , port : 20883] sayName("Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz)") : Hello,Little Horse Brother (mercyblitz")
The result is likewise running normally with load balancing. However, due to the absence of the demo.service.name property in the current example, the “name” part of the output is null. For more information, please refer to: https://github.com/apache/dubbo/tree/master/dubbo-registry/dubbo-registry-nacos.
If you are interested in or appreciate open-source projects like Dubbo and Nacos, feel free to give them a “star” to support:
- Apache Dubbo: https://github.com/apache/dubbo
- Dubbo Nacos Registry: https://github.com/apache/dubbo/tree/master/dubbo-registry/dubbo-registry-nacos
- Alibaba Nacos: https://github.com/alibaba/nacos