Dubbo Admin service test
Based on the metadata of Dubbo2.7, Dubbo Admin implements the service test function, which can call the real service provider on the console through generalized call.
Usage
Deploy the provider: You can download the demo here. This project is based on Spring Boot, which is convenient to start in the IDE or command line. For service testing, you only need to start
dubbo-basic-provider.Service-seeking: After completing the server deployment, you can query the corresponding service on the Dubbo Admin’s
service testpage: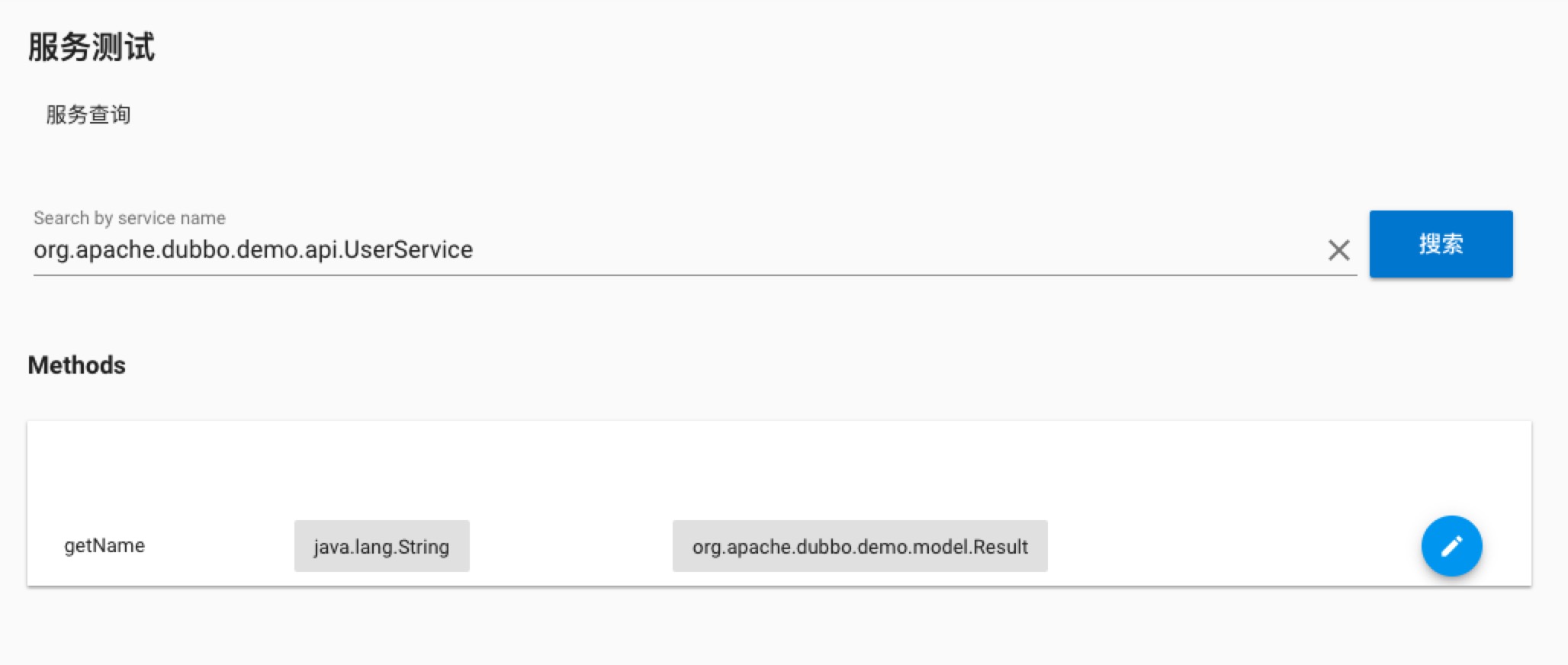
the information here is similar to the metadata, including the method name, parameter type and return value. Click the label on the right to enter theservice testpage.Service test:
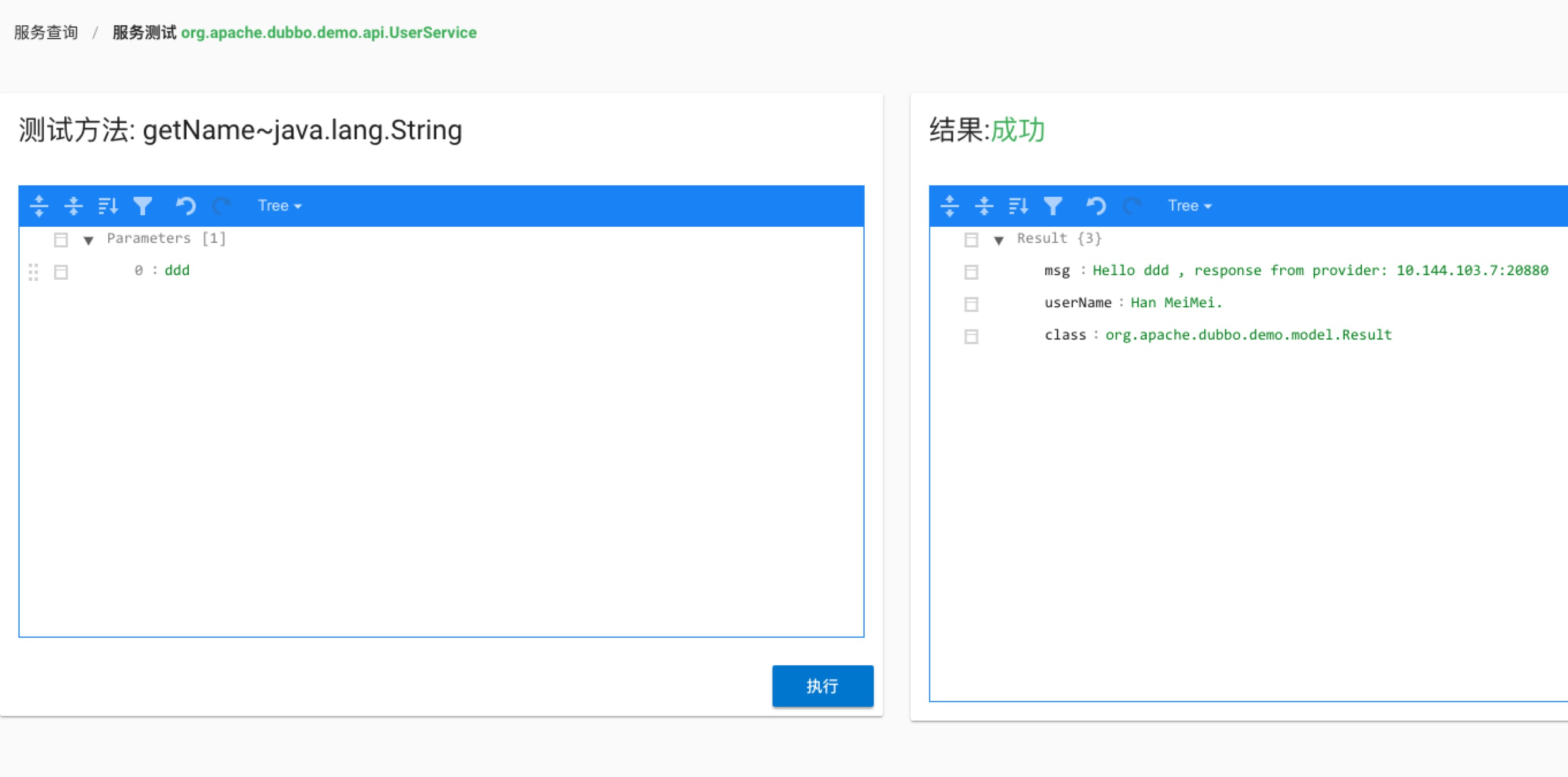
service testpage contains two json editor, the parameter’s informations are all stored in a json format, where you need to fill in the corresponding parameter values (in this case, the number type is String ), after filling, clickexecuteto initiate the call to the server, and the result of the call is displayed in the editor on the right. If the call fails, the detailed cause of the failure is displayed. Let’s look at the example of the call failure.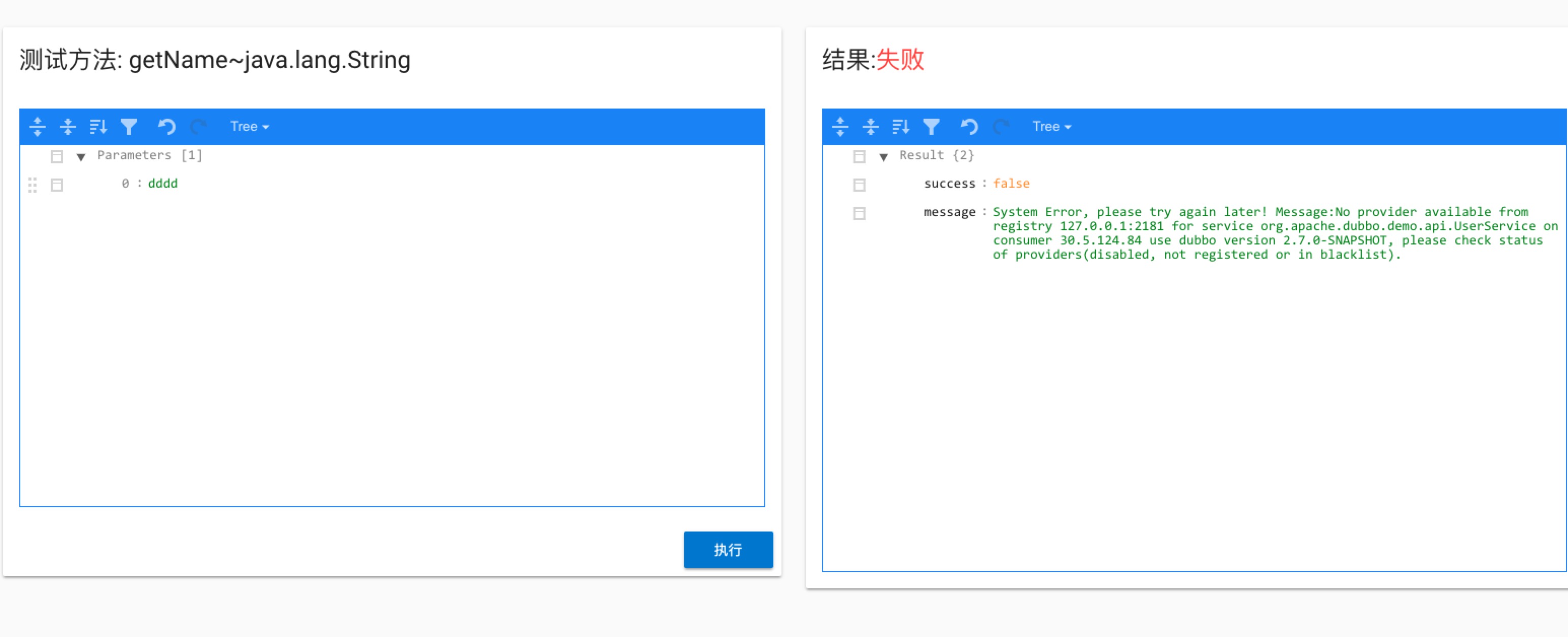
In this case, the Dubbo service provider’s process is shut down before the service test is executed, you can see that the returned result is an
No provider availbleexception. As with normal calls, business and framework exceptions are returned in the results, for easy business troubleshooting.Complex type parameters
Consider the following methods and types inUserService:
//org.apache.dubbo.demo.api.UserService
Result getUser(String name, UserInfoDO userInfoDO);
public class UserInfoDO {
private int id;
private LocationDO locationDO;
private DepartmentDO departmentDO;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "UserInfoDO{" +
"id=" + id +
", locationDO=" + locationDO.toString() +
", departmentDO=" + departmentDO.toString() +
'}';
}
}
public class DepartmentDO {
private String departName;
private LocationDO departLocation;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "DepartmentDO{" +
"departName='" + departName + '\'' +
", departLocation=" + departLocation.toString() +
'}';
}
}
public class LocationDO {
private String address;
private int postNum;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "LocationDO{" +
"address='" + address + '\'' +
", postNum=" + postNum +
'}';
}
}
The parameters are complex complex type. When the service is tested, the value of each field will be filled out layer by layer, As shown below: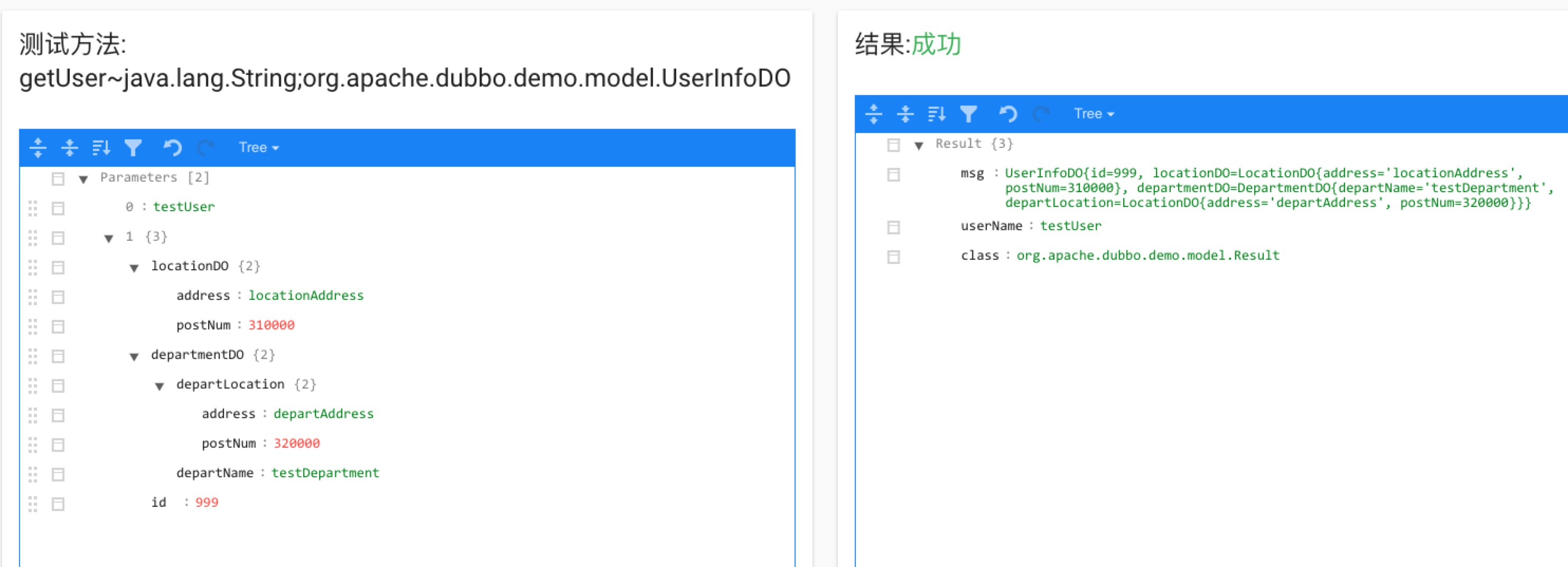 It can also make successful call and the result is returned.
It can also make successful call and the result is returned.
Principle:Data source
In the service test, the most important thing is the complete method signature, and the type information of the parameters, with which the values of each parameter can be filled step by step to assemble the complete service consumer. In Dubbo 2.7, the metadata center has been added. The method signature and parameter type information of Dubbo Admin is from here: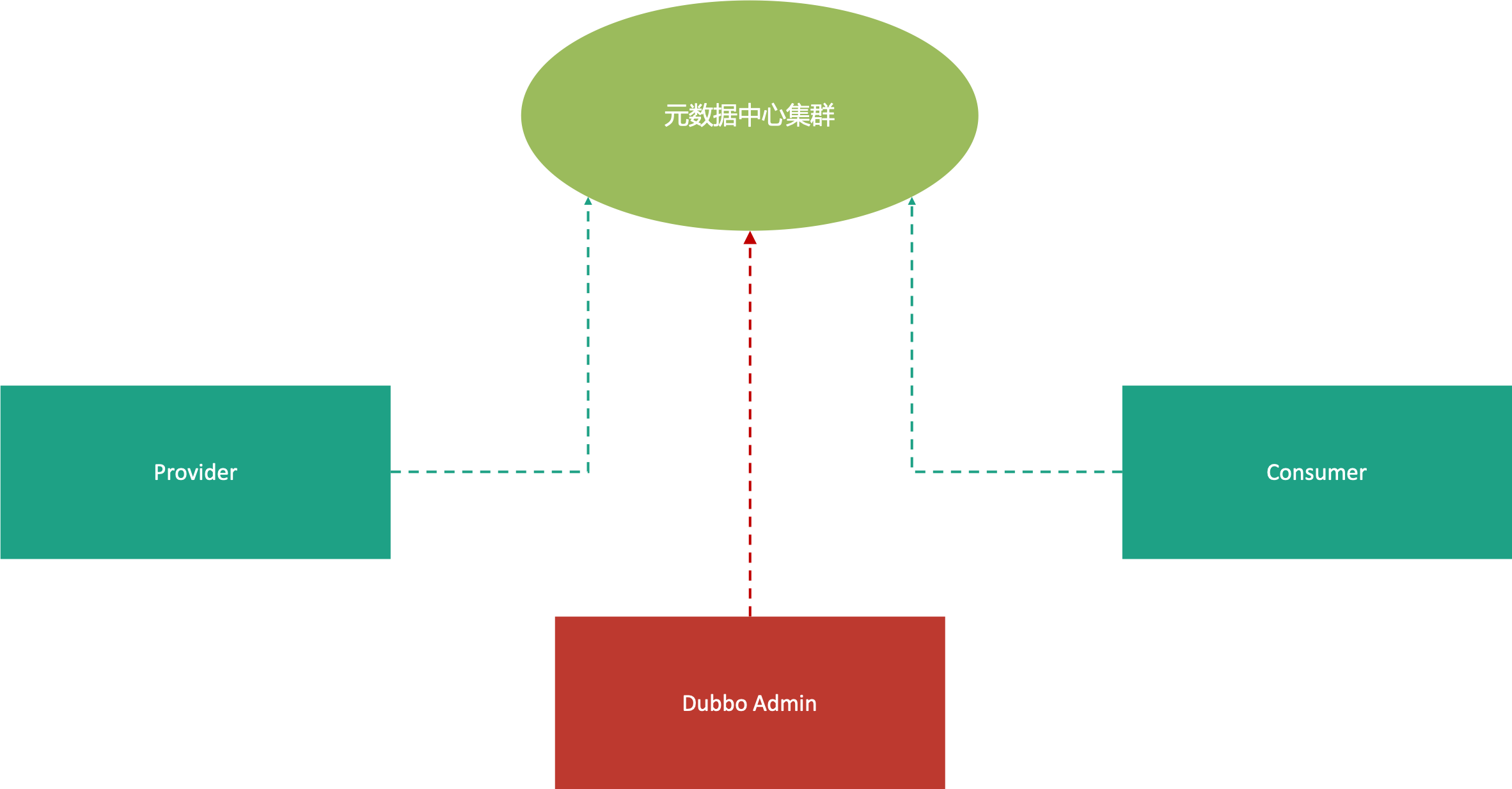 As shown, the server will register the metadata information of the service to the metadata center when it runs,the format is as follows:
As shown, the server will register the metadata information of the service to the metadata center when it runs,the format is as follows:
{
...
"methods": [
{
"name": "sayHello",
"parameterTypes": [
"org.apache.dubbo.demo.model.User"
],
"returnType": "org.apache.dubbo.demo.model.Result"
},
...
],
"types": [
{
"type": "char"
},
{
"type": "long"
},
{
"type": "org.apache.dubbo.demo.model.Result",
"properties": {
"msg": {
"type": "java.lang.String",
"properties": {
"value": {
"type": "char[]"
},
"hash": {
"type": "int"
}
}
},
"userName": {
"type": "java.lang.String",
"properties": {
"value": {
"type": "char[]"
},
"hash": {
"type": "int"
}
}
}
}
},
{
"type": "org.apache.dubbo.demo.model.User",
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "java.lang.Long",
"properties": {
"value": {
"type": "long"
}
}
},
"username": {
"type": "java.lang.Sring",
"properties": {
"value": {
"type": "char[]"
},
"hash": {
"type": "int"
}
}
}
}
},
...
]
}
Related to service testing is the method and type information contained in methods and types. Based on this information, Dubbo Admin renders the parameters into the Json Editor of the service test page, where the user enters the values of each parameter and each member variable.
Principle: Generalized calls
With the parameter type, the next question is how to call to the server. In the traditional Dubbo RPC call, the client needs to rely on the server’s API jar package ( refer to the dubbo-basic-consumer in the previous demo ), which is unlikely for Dubbo Admin, because the up and down of services are dynamic, Dubbo Admin can not dynamically increase the jar package dependencies, so you need to use the generalization call in Dubbo , which means that in the absence of the server API interface, the client initiates a service call through the GenericService interface, and the data objects in return values are represented by maps. The generalization call doesn’t require special processing on the server side, only need to be initiated by the client side.
Summary and outlook
This article briefly introduces the usage and principle of service testing, and will further enhance this function in the future, such as processing the parameter types of abstract classes, importing parameter values from json files, supporting the saving of parameter values, etc., to facilitate regression testing of the service interface.
